The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial component of the nervous system that plays a significant role in various bodily functions. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and related disorders is essential for comprehending its importance. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the glossopharyngeal nerve, including its location, functions, and its association with the central nervous system.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
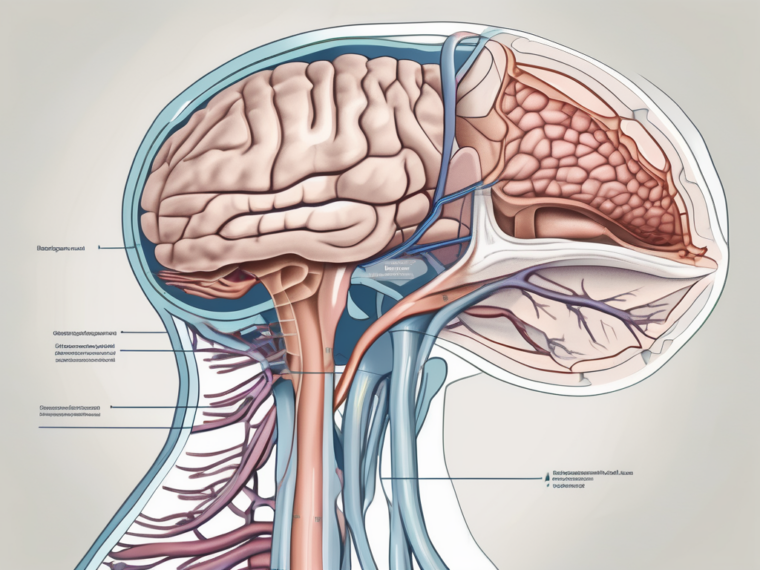
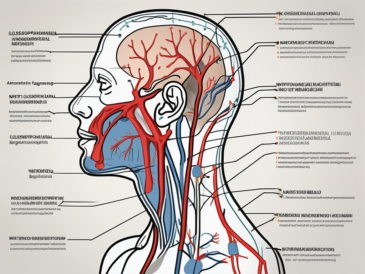
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is one of the twelve cranial nerves originating from the brainstem. It emerges from the medulla oblongata, the lower part of the brainstem, and consists of both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers arise from the superior and inferior glossopharyngeal ganglia, while the motor fibers connect to the stylopharyngeus muscle.
As it travels through the skull, the glossopharyngeal nerve branches into various smaller nerves that innervate specific areas, such as the tongue, pharynx, and inner ear. These branches allow for the complex functions associated with taste, swallowing, and sensation in the posterior part of the tongue and throat.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a fascinating structure with intricate connections. It is responsible for transmitting vital information from the brain to different parts of the body, enabling us to perform essential functions such as tasting, swallowing, and sensing touch and pain.
When we think about taste, we often associate it with the taste buds on our tongue. However, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a significant role in taste sensation as well. It carries signals related to taste from the posterior third of the tongue, allowing us to experience the flavors of various foods and beverages.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is involved in the sensation of touch and pain in the oropharynx and tonsils. It enables us to perceive sensations in these areas, alerting us to potential issues or discomfort.
But the glossopharyngeal nerve’s functions extend beyond taste and sensation. It also has a role in regulating blood pressure and cardiovascular homeostasis. By relaying signals to the brainstem, the glossopharyngeal nerve helps maintain a stable blood pressure level, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve serves multiple essential functions within the human body. As a sensory nerve, it carries signals related to taste sensation, touch, and pain from the posterior third of the tongue, the oropharynx, and the tonsils. Additionally, it provides sensory input from the carotid body, which monitors the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
Moving beyond sensory functions, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a role in swallowing as it stimulates the muscles involved in this intricate process. It also participates in regulating blood pressure by relaying signals to the brainstem, contributing to cardiovascular homeostasis.
Understanding the glossopharyngeal nerve’s functions is crucial in comprehending the complexity of our body’s neural network. By exploring its role in taste, sensation, swallowing, and blood pressure regulation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that allow us to experience and maintain our overall well-being.
Locating the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Position in the Human Body
Locating the glossopharyngeal nerve requires understanding its path through the head and neck region. The nerve initially descends alongside the other cranial nerves, crossing the jugular vein and passing through the jugular foramen. From there, it travels to the back of the tongue and pharynx to fulfill its various functions.
As the glossopharyngeal nerve makes its way through the head and neck, it navigates a complex network of tissues and structures. It intertwines with blood vessels, muscles, and other nerves, creating a intricate web of connections. This intricate pathway ensures that the nerve can effectively transmit signals and carry out its essential functions.
When it comes to pinpointing the exact location of the glossopharyngeal nerve, it is crucial to rely on the expertise of medical professionals. Doctors, neurologists, or other qualified healthcare providers possess the necessary knowledge and diagnostic tools to accurately identify the nerve and assess its condition when necessary.
Medical imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans can provide detailed visualizations of the head and neck anatomy, aiding in the identification and localization of the glossopharyngeal nerve. These advanced imaging technologies allow healthcare professionals to precisely map out the nerve’s course and evaluate any potential abnormalities or injuries.
Relation to Other Nerves
The glossopharyngeal nerve shares proximity with other vital structures within the head and neck region. One notable neighbor is the vagus nerve, or cranial nerve X, which also originates in the medulla oblongata. The glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves have intertwined functions, leading to their close association when it comes to certain physiological processes, particularly those involving the throat and larynx.
Together, the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves play a crucial role in regulating swallowing, speech, and the reflexes of the throat and larynx. These nerves work in harmony to coordinate the complex movements required for these essential functions. Dysfunction or damage to either nerve can lead to difficulties in swallowing, hoarseness, or other voice-related problems.
Understanding the relation between the glossopharyngeal nerve and its neighboring nerves highlights the complexity of the nervous system. It also emphasizes the importance of seeking professional medical guidance for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Medical professionals with expertise in neurology and otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat) can evaluate the function and integrity of the glossopharyngeal nerve, providing appropriate interventions and therapies when needed.
Research continues to uncover new insights into the intricate workings of the glossopharyngeal nerve and its interactions with other nerves and structures. This ongoing exploration helps expand our understanding of the human body and contributes to advancements in medical knowledge and treatments for conditions affecting the head and neck region.
Disorders Related to the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a cranial nerve that plays a crucial role in various functions related to the throat and tongue. When this nerve is damaged or affected by a disorder, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Damage
Glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can manifest in various ways, depending on the severity and specific location of damage. One common symptom is difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia. This can make it challenging to eat or drink, leading to weight loss and malnutrition if not properly managed.
Another symptom of glossopharyngeal nerve damage is an altered taste sensation. This can result in a persistent metallic or bitter taste in the mouth, making it difficult to enjoy food and beverages. Additionally, some individuals may experience a loss of taste altogether, affecting their ability to savor flavors and detect potential dangers, such as spoiled food.
Pain in the throat or tongue is another prevalent symptom of glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, sharp sensations that make it difficult to speak, eat, or even swallow saliva. The intensity and duration of the pain can vary depending on the underlying cause of the nerve damage.
It is important to note that these symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and overall well-being. Therefore, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
Treatment strategies for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, medical interventions or surgical procedures might be necessary to address the issue or alleviate associated symptoms.
For individuals with dysphagia, speech and swallowing therapy can be beneficial. These therapies aim to improve the coordination and strength of the muscles involved in swallowing, allowing for a safer and more efficient swallowing process. In severe cases, a feeding tube may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition and hydration.
When altered taste sensation is a significant concern, working with a nutritionist or dietitian can be helpful. They can provide guidance on how to enhance flavors through alternative seasonings and cooking techniques, ensuring a more enjoyable eating experience despite the taste changes.
Pain management is a crucial aspect of treating glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Depending on the severity of the pain, over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended. Additionally, certain nerve blocks or injections can provide temporary relief by targeting the specific area affected by the nerve damage.
It is essential to emphasize that the appropriateness of any treatment should be determined by a healthcare provider. They will consider the individual’s specific condition, medical history, and overall health before recommending a course of action.
In conclusion, glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can lead to various symptoms, including difficulty swallowing, altered taste sensation, and throat or tongue pain. Seeking medical attention and appropriate treatment is crucial for managing these conditions and improving overall quality of life.
The Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Nervous System
Interactions with the Central Nervous System
The glossopharyngeal nerve is an integral part of the central nervous system, facilitating communication between various structures and the brain. Through its connections with the brainstem, the nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining sensory and motor functions in the head and neck region.
One of the key interactions of the glossopharyngeal nerve with the central nervous system is its connection with the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus, often referred to as the “control center” of the brain, regulates numerous bodily functions, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep. The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a role in relaying sensory information related to these functions to the hypothalamus, allowing for appropriate responses and adjustments.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is also involved in the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. This nerve contributes to the regulation of cardiovascular activity and hormonal balance, ensuring the body maintains homeostasis.
Contribution to Sensory and Motor Functions
The functions associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve are instrumental in maintaining overall well-being. Sensory stimulation from the tongue and oropharynx helps in the enjoyment of food and beverages while alerting the body to potential danger or abnormalities. The taste buds on the back of the tongue, innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve, allow us to experience the diverse flavors of different foods, enhancing our culinary experiences.
In addition to its sensory role, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a crucial role in motor functions, particularly in the complex process of swallowing. When we eat or drink, the glossopharyngeal nerve coordinates the movement of various muscles involved in swallowing, ensuring that food and liquids safely pass through the throat and into the esophagus. This motor function promotes proper nutrition and hydration, supporting overall health and well-being.
Understanding the contributions of the glossopharyngeal nerve to sensory and motor functions allows us to appreciate its significance and the potential impact of related disorders on daily life. Disorders affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve can lead to difficulties in swallowing, loss of taste sensation, and other complications that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Further research and understanding of this nerve’s role in the nervous system can aid in the development of effective treatments and interventions for such conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial component of the human nervous system, responsible for various important functions. As with any complex physiological topic, misconceptions surrounding the glossopharyngeal nerve can arise. It is important to address and correct these misconceptions, as they can lead to misinformation and misunderstandings.
One common misconception is that the glossopharyngeal nerve is only involved in the sense of taste. While it does play a role in transmitting taste signals from the back of the tongue, it also has other significant functions. For instance, the glossopharyngeal nerve is involved in the sensation of touch and pain in the throat, as well as the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate.
Engaging with knowledgeable healthcare professionals to seek accurate information can help dispel any misconceptions and ensure a clear understanding of the topic. These professionals can provide valuable insights into the complexities of the glossopharyngeal nerve and its role in maintaining overall health.
Common Misconceptions about the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
It is essential to address some common misconceptions about the glossopharyngeal nerve to promote accurate knowledge and understanding. One prevalent misconception is that damage to this nerve only affects taste perception. While taste disturbances can occur, damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can also lead to difficulties in swallowing, speaking, and even breathing.
Another misconception is that the glossopharyngeal nerve is not as important as other cranial nerves. In reality, this nerve is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of various bodily systems. It plays a vital role in transmitting sensory information from the throat, tongue, and other areas to the brain, allowing for appropriate responses and regulation of bodily functions.
Understanding the misconceptions surrounding the glossopharyngeal nerve is key to ensuring accurate knowledge and dispelling any false beliefs. By seeking information from reliable sources and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of this important nerve and its implications for overall health.
The Future of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Research
Advancements in research and technology offer promising possibilities for enhancing our understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Ongoing studies focus on elucidating the nerve’s role in various physiological processes, exploring potential treatment options for associated disorders, and discovering ways to improve the overall functioning of the nervous system.
Researchers are investigating the intricate connections between the glossopharyngeal nerve and other cranial nerves, aiming to unravel the complex interplay that contributes to the overall functioning of the nervous system. By gaining a deeper understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve’s interactions, scientists hope to develop targeted therapies for conditions such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, a rare but debilitating disorder characterized by severe throat and ear pain.
Furthermore, advancements in neuroimaging techniques allow researchers to visualize the glossopharyngeal nerve and its connections with greater precision. This enables a more detailed examination of its structure and function, paving the way for improved diagnostic methods and treatment approaches.
Remember, when it comes to matters pertaining to the glossopharyngeal nerve or any other aspect of health, always consult with qualified medical professionals for accurate information, diagnosis, and treatment options tailored to your specific circumstances. The future of glossopharyngeal nerve research holds great promise, and staying informed about the latest developments can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.