The glossopharyngeal nerve is an important cranial nerve that plays a significant role in various bodily functions. Understanding the anatomy, functions, disorders, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and prevention and management techniques related to this nerve is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge of the human nervous system. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the glossopharyngeal nerve, shedding light on its multifaceted nature and providing valuable insights into its clinical significance and implications.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
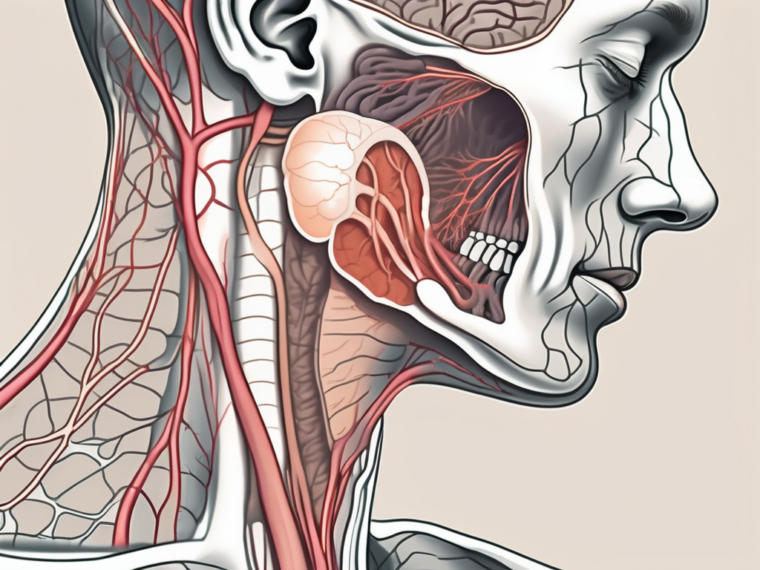
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, emerges from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. It originates from the inferior ganglion, and upon leaving the skull through the jugular foramen, it traverses the neck, accompanying the carotid artery.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a complex structure with intricate connections. It is composed of both sensory and motor fibers, making it a vital component of the nervous system. The sensory fibers of this nerve innervate the posterior one-third of the tongue, the oropharynx, and the carotid sinus. These sensory impulses play a crucial role in our ability to taste, perceive touch and temperature sensations in the back of the tongue, and maintain the baroreceptor reflex, which regulates blood pressure and heart rate.
On the other hand, the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve control the stylopharyngeus muscle. This muscle is responsible for various functions, including aiding in swallowing and contributing to the gag reflex. The coordinated movements facilitated by the motor impulses transmitted by the glossopharyngeal nerve ensure the smooth functioning of these essential processes.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Working in tandem with other cranial nerves, the glossopharyngeal nerve serves crucial functions that are fundamental to our daily lives. Sensory impulses carried by this nerve allow us to taste a wide array of flavors, from the sweetness of a ripe fruit to the bitterness of dark chocolate. These sensory signals are transmitted from the taste buds on the posterior one-third of the tongue to the brain, where they are interpreted and contribute to our overall sensory experience.
In addition to taste, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a role in touch and temperature sensations in the back of the tongue. This allows us to discern the texture and temperature of the food we consume, enhancing our enjoyment and ensuring our safety by alerting us to potential hazards, such as hot liquids or sharp objects.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is involved in the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate through the baroreceptor reflex. Baroreceptors, located in the carotid sinus, detect changes in blood pressure and send signals to the brain via the glossopharyngeal nerve. In response, the brain initiates appropriate adjustments to maintain optimal blood flow and cardiovascular function.
Moving on to the motor functions, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in the process of swallowing. As we consume food and liquids, the muscles of the throat and esophagus work in harmony to transport the bolus from the mouth to the stomach. The stylopharyngeus muscle, controlled by the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve, contributes to the coordinated movements required for efficient swallowing.
In addition to swallowing, the glossopharyngeal nerve aids in the protection of the airway. The gag reflex, triggered by stimulation of the back of the throat, is an important defense mechanism that helps prevent choking and aspiration of foreign objects. The motor impulses transmitted by the glossopharyngeal nerve play a crucial role in initiating the gag reflex, ensuring the safety of the respiratory system.
It is important to note that dysfunction or damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can lead to a range of troublesome symptoms and conditions. These may include difficulty swallowing, loss of taste sensation, impaired blood pressure regulation, and compromised airway protection. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in managing these conditions and restoring optimal functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Disorders Associated with the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial cranial nerve responsible for various functions related to the throat and tongue. It plays a vital role in swallowing, taste sensation, and speech. However, certain disorders and injuries can affect the proper functioning of this nerve, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a rare and often misunderstood disorder characterized by intense, paroxysmal pain in the distribution of the glossopharyngeal nerve. The pain is typically triggered by activities like swallowing, speaking, or yawning. It can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Individuals experiencing glossopharyngeal neuralgia may find relief with medication or more invasive medical interventions. Medications such as anticonvulsants or tricyclic antidepressants can help alleviate the pain. In severe cases, surgical procedures like microvascular decompression or nerve blocks may be considered. However, each treatment option should be carefully evaluated and discussed with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable approach for the individual.
Damage and Injury to the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Damage or injury to the glossopharyngeal nerve can occur due to various factors, such as trauma, tumors, infections, or underlying medical conditions. The consequences of such damage can be significant and may affect multiple aspects of a person’s daily life.
One common symptom of glossopharyngeal nerve damage is difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia. This can make it challenging to eat and drink, leading to weight loss and malnutrition if not properly managed. Additionally, damage to the nerve can result in a loss of taste sensation, making food less enjoyable and potentially affecting a person’s appetite.
Speech abnormalities can also arise from glossopharyngeal nerve damage. The nerve plays a crucial role in the coordination of various muscles involved in speech production. When injured, these muscles may not function properly, leading to difficulties in articulation and pronunciation.
Seeking prompt medical attention and undergoing diagnostic procedures can aid in determining the extent and cause of the damage. Imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, may be performed to identify any structural abnormalities or lesions affecting the nerve. Once a diagnosis is made, appropriate management and treatment options can be explored.
Physical therapy and speech therapy may be recommended to help restore function and improve swallowing and speech abilities. In some cases, surgical interventions, such as nerve repair or grafting, may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the damage and restore nerve function.
In conclusion, disorders and injuries associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia can cause excruciating pain, while damage to the nerve can result in difficulties with swallowing, loss of taste sensation, and speech abnormalities. Seeking medical attention and exploring appropriate treatment options are essential for managing these conditions and improving overall quality of life.
Diagnostic Procedures for Glossopharyngeal Nerve Conditions
Clinical Examination Techniques
When investigating potential glossopharyngeal nerve conditions, healthcare professionals may employ clinical examination techniques to assess the patient’s symptoms, perform neurological examinations, and rule out other possible causes. Such examinations can aid in determining the precise origin and nature of the symptoms, facilitating accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
During a clinical examination, the healthcare provider will carefully evaluate the patient’s medical history, paying close attention to any previous injuries, illnesses, or surgeries that may have affected the glossopharyngeal nerve. They will also inquire about the specific symptoms experienced, such as difficulty swallowing, throat pain, or changes in taste sensation.
In addition to the medical history, the healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, focusing on the head, neck, and throat regions. They may gently palpate the neck to check for any abnormalities or tenderness. The provider will also assess the patient’s ability to swallow by observing their swallowing movements and listening for any abnormal sounds.
Furthermore, the healthcare provider may conduct a neurological examination to evaluate the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve. This may involve testing the patient’s ability to taste different substances, assessing their gag reflex, and evaluating their ability to move the muscles of the tongue and throat.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, healthcare providers may deem it necessary to conduct imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, to obtain detailed visualizations of the cranial structures. These imaging techniques can help identify any structural abnormalities or lesions that may be affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve.
During an MRI or CT scan, the patient will lie on a table that slides into a large, tunnel-like machine. The machine will then generate detailed images of the head and neck, allowing the healthcare provider to examine the cranial structures and identify any potential issues.
Additionally, laboratory tests may be employed to gather valuable information about the patient’s condition and to assist with diagnosis and treatment planning. Blood tests can provide insights into the patient’s overall health and detect any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the glossopharyngeal nerve symptoms.
Electromyography (EMG) is another diagnostic test that may be used to assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve. During an EMG, small electrodes are inserted into the muscles of the throat to measure their electrical activity. This test can help determine if there is any nerve damage or dysfunction affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve.
In conclusion, the diagnostic procedures for glossopharyngeal nerve conditions involve a combination of clinical examination techniques, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. These procedures are crucial in accurately diagnosing and treating patients with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders, allowing healthcare providers to develop appropriate treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Treatment Options for Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
Glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can be debilitating and greatly impact a person’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to manage these conditions and alleviate symptoms. In addition to medication therapies and surgical interventions, there are other approaches that can be explored to provide relief and improve overall well-being.
Medication Therapies
In many cases, glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can be effectively managed through conservative measures, such as medication therapies. These may include the use of analgesics to alleviate pain or antiepileptic drugs to reduce nerve excitability. Analgesics, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids, can help relieve the intense pain associated with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Antiepileptic drugs, such as gabapentin or carbamazepine, can help stabilize nerve activity and reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
However, the choice of medication and dosage should be determined by a qualified healthcare professional after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s specific condition and medical history. It is important to consider potential side effects, drug interactions, and individual response to treatment when prescribing medication therapies for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
Surgical Interventions
In more severe or refractory cases, surgical interventions may be considered as a treatment option. Surgical procedures, such as microvascular decompression or neurectomy, aim to alleviate pressure on the glossopharyngeal nerve or selectively interrupt pain signals. Microvascular decompression involves repositioning or removing blood vessels that are compressing the nerve, while neurectomy involves surgically cutting or removing a portion of the nerve.
It is imperative to consult with a specialist in neurosurgery or otolaryngology to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and long-term outcomes associated with surgical interventions for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. These procedures are typically reserved for cases where conservative measures have failed to provide adequate relief or when the condition significantly impairs daily functioning.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to medication therapies and surgical interventions, there are alternative therapies that can complement traditional treatment approaches for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. These therapies focus on promoting overall well-being, reducing stress, and improving the body’s ability to cope with pain.
One such alternative therapy is acupuncture, which involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote healing. Acupuncture has been shown to provide pain relief and improve symptoms in some individuals with nerve-related disorders.
Another alternative therapy that may be beneficial is physical therapy. Physical therapists can design customized exercise programs to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and posture, which can help alleviate pain and improve overall function. They may also use techniques such as manual therapy, electrical stimulation, or ultrasound to target specific areas affected by glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
Additionally, complementary approaches such as relaxation techniques, meditation, and biofeedback can help individuals manage stress, reduce muscle tension, and promote a sense of calmness. These techniques can be learned through specialized training programs or with the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
It is important to note that alternative therapies should be used in conjunction with, not as a replacement for, conventional medical treatments. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any alternative therapy to ensure its safety and appropriateness for individual circumstances.
In conclusion, glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can be effectively managed through a combination of medication therapies, surgical interventions, and alternative therapies. The choice of treatment should be based on the severity of symptoms, individual response to treatment, and the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals. With the right approach, individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can find relief and improve their overall quality of life.
Prevention and Management of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in the prevention and management of glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Avoiding factors that may trigger pain, such as hot or cold temperatures or certain food items, can help minimize symptoms. Adapting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep can also contribute to overall wellbeing and potentially reduce the likelihood of developing certain nerve-related conditions.
When it comes to managing glossopharyngeal nerve disorders, lifestyle modifications can be a powerful tool. By making simple changes to your daily routine, you can significantly improve your quality of life. For example, if you find that hot or cold temperatures exacerbate your symptoms, you can take steps to protect yourself. This could involve wearing appropriate clothing to shield yourself from extreme temperatures or avoiding environments that are known to be excessively hot or cold.
Furthermore, paying attention to your diet can make a big difference. Certain food items, such as spicy or acidic foods, can trigger symptoms in individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, you can minimize discomfort and prevent flare-ups. It may be helpful to consult with a nutritionist or dietitian who can provide guidance on creating a well-balanced diet that supports your overall health and addresses your specific needs.
Engaging in regular exercise is another lifestyle modification that can benefit individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Exercise has been shown to have numerous positive effects on the body, including reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and promoting overall wellbeing. Incorporating activities that you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, into your routine can help manage symptoms and enhance your overall quality of life.
Stress management techniques are also crucial for individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Stress has been linked to the exacerbation of symptoms in many neurological conditions, including those affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress, such as practicing mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy, can help reduce symptom severity and improve your overall mental and physical wellbeing.
Lastly, ensuring adequate sleep is essential for individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Sleep plays a vital role in the body’s healing and restoration processes. It is during sleep that the body repairs damaged tissues and replenishes energy levels. By prioritizing sleep and establishing a consistent sleep routine, you can support your body’s natural healing mechanisms and promote optimal nerve function.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
For individuals experiencing functional limitations or muscle weakness due to glossopharyngeal nerve disorders, physical therapy and rehabilitation may be beneficial. These specialized interventions focus on enhancing muscle strength and coordination, improving swallowing function, and optimizing overall oral health. A skilled physical therapist or rehabilitation specialist can design a customized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals.
Physical therapy for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders typically involves a combination of exercises, manual therapy techniques, and functional training. The goal is to improve muscle strength and coordination in the affected areas, such as the throat and mouth, to enhance swallowing function and reduce symptoms of dysphagia. The physical therapist may also incorporate techniques to improve oral health, such as tongue exercises and proper oral hygiene practices.
In addition to the physical aspects, rehabilitation for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders also addresses the emotional and psychological impact of the condition. Coping strategies, counseling, and support groups may be incorporated into the treatment plan to help individuals navigate the challenges and emotional toll that can accompany living with a neurological disorder.
It is important to note that physical therapy and rehabilitation should be conducted under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. They will assess your specific condition, evaluate your functional limitations, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your unique needs. Regular follow-up appointments will allow for progress monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary.