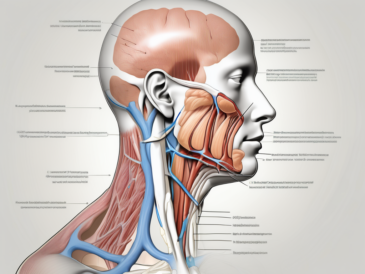
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, plays a crucial role in the sensory functions of the oral cavity and throat. Understanding the complex anatomy and functions of this nerve is essential for gaining insights into its sensory contributions. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the glossopharyngeal nerve, explore its role in the nervous system, examine its sensory functions, discuss disorders related to this nerve, and explore treatment options. Additionally, we will look at the future of glossopharyngeal nerve research and its potential implications for understanding sensory functions.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, emerges from the medulla oblongata, a region of the brainstem responsible for controlling vital functions. It is one of the twelve cranial nerves and is considered a mixed nerve, containing both motor and sensory fibers. While the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate the stylopharyngeus muscle, which plays a crucial role in swallowing and speech production, our focus will be on the sensory functions of this remarkable nerve.
The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve originate from specialized sensory receptors present in the oral cavity and throat. These receptors, known as taste buds, detect various sensations, such as taste, touch, and temperature. They are scattered across the tongue, the back of the throat, and even extend into the middle ear. The signals generated by these receptors are then transmitted through the glossopharyngeal nerve to the brain, providing us with important sensory information about the world around us.
Interestingly, the glossopharyngeal nerve is not solely responsible for taste perception. It also carries sensory information related to pain, pressure, and other tactile sensations from the oral cavity and throat. This diverse range of sensory input allows us to experience the pleasure of a delicious meal, the discomfort of a sore throat, or the sensation of a hot beverage warming our mouth.
Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Nervous System
Within the intricate network of the nervous system, the glossopharyngeal nerve connects with various areas of the brain, including the medulla oblongata and the solitary nucleus. These regions are involved in processing and integrating sensory information from different parts of the body. The connection between the glossopharyngeal nerve and these brain areas allows for the interpretation and analysis of the sensory stimuli received from the oral cavity and throat.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve interacts with other cranial nerves involved in sensory processing, such as the trigeminal nerve and the vagus nerve. This intricate interplay ensures the smooth coordination of sensory information between different areas of the nervous system, contributing to an accurate perception of sensory stimuli. For example, the trigeminal nerve, responsible for facial sensation, works in conjunction with the glossopharyngeal nerve to provide a comprehensive sensory experience when we taste, chew, or speak.
It is worth noting that the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a role in regulating certain autonomic functions, such as blood pressure and heart rate. It carries sensory information from specialized receptors located in the carotid sinus, a small structure in the neck that helps monitor blood pressure. This information is then relayed to the brain, which can initiate appropriate responses to maintain cardiovascular homeostasis.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable cranial nerve that not only enables us to taste and perceive sensations in the oral cavity and throat but also contributes to the complex interplay of sensory information within the nervous system. Its connections with various brain regions and other cranial nerves ensure the accurate processing and interpretation of sensory stimuli, allowing us to fully experience the world around us.
Sensory Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Taste Sensation and the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
One of the primary sensory functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve is its involvement in taste sensation. The nerve carries taste signals from specialized taste buds located at the back of the tongue and the upper throat. These taste buds are responsible for detecting the different tastes, such as sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
Through the glossopharyngeal nerve, the brain receives taste signals from the back of the tongue. This information helps in distinguishing flavors, enhancing the overall sensory experience during eating and drinking.
When you take a bite of your favorite dessert, the glossopharyngeal nerve springs into action, relaying the delightful taste of sweetness to your brain. It allows you to savor the rich, velvety texture of chocolate cake or the refreshing tang of a lemonade on a hot summer day. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, the world of flavors would be dull and unexciting.
Imagine biting into a juicy, ripe strawberry. As the sweet juices burst on your taste buds, the glossopharyngeal nerve sends signals to your brain, creating a symphony of taste sensations. The nerve allows you to appreciate the subtle differences between the sweetness of a strawberry and the tartness of a pineapple.
Sensing Changes in Blood Pressure
Besides its role in taste sensation, the glossopharyngeal nerve also contributes to monitoring changes in blood pressure. Specialized cells in the carotid artery, known as baroreceptors, detect changes in blood pressure. The glossopharyngeal nerve carries information from these baroreceptors to the brain, which helps in maintaining stable blood pressure levels.
By detecting changes in blood pressure, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the body’s ability to respond and regulate blood pressure accordingly. This function is crucial for overall cardiovascular health and ensuring the proper functioning of vital organs.
Imagine you’re going for a run, and your heart starts pounding, pumping blood faster to supply oxygen to your working muscles. The glossopharyngeal nerve senses this increase in blood pressure, alerting your brain to the need for more oxygen. As a result, your body adjusts by increasing the rate and depth of your breathing, ensuring that your muscles receive the oxygen they require to keep you going.
Similarly, when you’re in a state of deep relaxation, the glossopharyngeal nerve detects the decrease in blood pressure. It signals your brain to slow down your heart rate, promoting a sense of calm and tranquility.
Role in Swallowing and Gag Reflex
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a key role in swallowing and the gag reflex. The sensory fibers of this nerve transmit information from the throat and trigger the appropriate motor responses involved in swallowing and preventing choking.
Next time you enjoy a delicious meal, take a moment to appreciate the intricate coordination between your glossopharyngeal nerve and the muscles involved in swallowing. As you chew and swallow, the nerve ensures that the food moves smoothly down your throat, avoiding any mishaps or discomfort.
In addition, the glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for initiating the gag reflex, a protective mechanism that helps prevent foreign objects from entering the airway. This reflex is essential for your safety, as it allows you to expel anything that may pose a threat to your breathing.
Imagine accidentally swallowing a fishbone while enjoying a meal. Thanks to the glossopharyngeal nerve, your body quickly responds with a gag reflex, triggering a series of muscular contractions to expel the bone and prevent it from causing harm.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable part of our nervous system, contributing to our ability to taste, monitor blood pressure, and ensure safe swallowing. Its intricate functions enhance our sensory experiences and protect our well-being, making it an essential component of our overall health.
Disorders Related to the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in the functioning of the throat, tongue, and ear. When this nerve is affected by certain disorders, it can lead to various symptoms and complications.
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition characterized by severe pain in the throat, tongue, and ear. It occurs due to irritation or compression of the glossopharyngeal nerve, leading to episodes of intense pain. The exact cause of glossopharyngeal neuralgia can vary, ranging from nerve damage to structural abnormalities or underlying medical conditions.
The pain experienced in glossopharyngeal neuralgia can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It may occur spontaneously or be triggered by activities such as swallowing, talking, or even touching certain areas of the face. The pain can be sharp, shooting, or burning in nature, and it may last for a few seconds to several minutes.
If you experience symptoms of glossopharyngeal neuralgia, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests, to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. Treatment options may include medications to alleviate pain, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
Damage and its Impact on Sensory Functions
The glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the throat, tongue, and ear to the brain. When this nerve is damaged, it can lead to various sensory disturbances, impacting functions such as taste sensation, swallowing, and the gag reflex.
Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can occur due to trauma, infections, tumors, or other medical conditions. The extent of sensory impairment may vary depending on the location and severity of the nerve damage. Some individuals may experience a partial loss of sensation, while others may completely lose certain sensory functions.
If you notice any changes in your sensory functions related to the oral cavity and throat, such as difficulty swallowing, altered taste perception, or a weakened gag reflex, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause and inform appropriate treatment strategies.
In some cases, rehabilitation techniques may be employed to help individuals regain or compensate for lost sensory functions. These techniques may include exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing, dietary modifications to ensure adequate nutrition, and sensory retraining to improve taste perception.
Overall, disorders related to the glossopharyngeal nerve can significantly impact a person’s daily life and well-being. Seeking timely medical intervention and following the recommended treatment plan can help manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Treatment and Management of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
Glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing pain and affecting sensory functions. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to manage these disorders and improve overall well-being.
Medications and Therapies
One of the primary approaches to treating glossopharyngeal nerve disorders is through the use of medications. Anticonvulsants and antidepressants are commonly prescribed to alleviate the pain associated with glossopharyngeal neuralgia and other nerve-related conditions. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of the disorder, helping to reduce pain and improve overall functioning.
In addition to medication, physical therapy and other supportive therapies may be recommended to address swallowing difficulties and improve oral and throat function. These therapies can involve a range of exercises and techniques aimed at strengthening the muscles involved in swallowing and restoring normal sensory functions. Speech therapists and occupational therapists can play a crucial role in guiding individuals through these therapies, providing expert guidance and support.
Furthermore, alternative therapies such as acupuncture and chiropractic care may also be considered as complementary approaches to managing glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. These therapies focus on promoting overall well-being and can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. Surgical options aim to alleviate compression or irritation on the nerve, thereby reducing pain and restoring normal sensory functions. Microvascular decompression, a surgical procedure that involves repositioning blood vessels causing compression on the nerve, is one such option. Other surgical interventions may include nerve blocks or neurectomy, which involve selectively blocking or removing the affected nerve.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual needs. A comprehensive evaluation will help guide the treatment plan, ensuring that the chosen interventions are tailored to address the specific challenges faced by each individual.
Living with a glossopharyngeal nerve disorder can be challenging, but with the right treatment and management strategies, individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and overall well-being. Ongoing support from healthcare professionals, therapists, and support groups can provide invaluable assistance throughout the journey towards recovery.
The Future of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Research
Advances in Neurology and Neuroscience
The field of neurology and neuroscience is continuously advancing, offering promising avenues for further understanding the functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve. Ongoing research focuses on unraveling the intricacies of sensory processing within the nervous system and exploring novel treatment approaches for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
Advancements in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional MRI, provide researchers with valuable insights into the brain regions associated with sensory processing. These advancements facilitate a better understanding of the complex interaction between the glossopharyngeal nerve and other sensory pathways.
One area of research that shows promise is the investigation of the role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in taste perception. Studies have shown that this nerve plays a crucial role in transmitting taste signals from the back of the tongue and throat to the brain. By understanding the specific mechanisms involved in taste perception, researchers hope to develop targeted interventions to address taste disorders and improve the overall sensory experience for individuals affected by glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
Another fascinating area of research is the exploration of the glossopharyngeal nerve’s role in cardiovascular regulation. This nerve is involved in monitoring blood pressure and heart rate, and any dysfunction in its function can lead to cardiovascular disorders. By studying the intricate connections between the glossopharyngeal nerve and the cardiovascular system, researchers aim to develop new therapeutic strategies for managing cardiovascular conditions and improving patient outcomes.
Potential Implications for Sensory Function Understanding
Improved understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve’s sensory contributions can have significant implications for the broader understanding of sensory functions within the nervous system. Insights gained from studying this nerve can potentially shed light on the mechanisms underlying taste perception, cardiovascular regulation, and swallowing processes.
Furthermore, such knowledge can aid in the development of targeted interventions and therapies to address sensory deficits and improve overall quality of life for individuals affected by glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
Research also suggests a potential link between the glossopharyngeal nerve and swallowing processes. This nerve plays a crucial role in coordinating the complex movements involved in swallowing, ensuring that food and liquids safely pass from the mouth to the esophagus. Understanding the precise mechanisms by which the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to swallowing can lead to advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of swallowing disorders, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in the sensory functions of the oral cavity and throat. By understanding its anatomy, role in the nervous system, and various sensory functions, we can appreciate its significance in our daily lives. Although disorders related to this nerve can cause sensory disturbances, prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical care can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. With ongoing research, the future holds promising advances in our understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve and its potential implications for sensory function understanding.