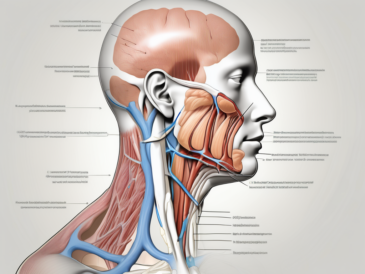
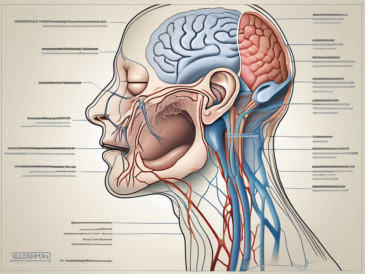
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, with a multitude of intricate connections and pathways. One such connection that often piques the curiosity of medical professionals and enthusiasts alike is the journey of the glossopharyngeal nerve to the parotid gland. Understanding this journey requires delving into the anatomy and function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, the role of the parotid gland, and the phenomenon of nerve hitchhiking in the nervous system.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
At the heart of the question lies the glossopharyngeal nerve, the ninth cranial nerve designated as cranial nerve IX. This nerve is responsible for a multitude of functions, primarily related to sensation and motor control in the oropharynx region. It is involved in processes such as swallowing, taste perception, and monitoring blood pressure.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the cranial nerve IX, is a fascinating component of the human nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and diverse functions make it a crucial player in the complex network of cranial nerves.
Let’s delve deeper into the anatomy of the glossopharyngeal nerve to gain a better understanding of its structure and origins.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve originates from the medulla oblongata, a critical part of the brainstem that controls vital functions. It emerges from the posterior cranial fossa and extends downwards, passing through various structures within the skull before reaching its destination.
Within the skull, the glossopharyngeal nerve traverses intricate pathways, intertwining with other cranial nerves and blood vessels. Its journey is a testament to the complexity and precision of the human nervous system.
The nerve comprises both sensory and motor components, with numerous branches supplying different regions. The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve carry information from the tongue, soft palate, pharynx, and other areas of the oropharynx to the brain. Meanwhile, the motor fibers control the contraction of certain muscles involved in swallowing and speech production.
Understanding the intricate anatomy of the glossopharyngeal nerve allows us to appreciate its role in the human body. It is a remarkable example of the precision and interconnectedness of our nervous system.
Function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
As mentioned previously, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Sensory branches of the nerve are responsible for transmitting taste sensations from the posterior third of the tongue. This is why damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can lead to a loss of taste in these particular regions.
But the functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve extend beyond taste perception. It is also involved in the complex process of swallowing, coordinating the movements of muscles in the oropharynx to ensure efficient and safe passage of food and liquids. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, the act of swallowing would be compromised, leading to difficulties in nourishment and hydration.
In addition to taste sensation and swallowing, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the reflex control of blood pressure. It monitors the carotid sinus, a small bulbous structure located within the carotid artery, and relays information to the brain. Consequently, any dysfunction in the glossopharyngeal nerve may disrupt blood pressure regulation, potentially leading to complications.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is truly a remarkable component of our nervous system. Its multifaceted functions highlight its importance in maintaining proper sensory perception, facilitating efficient swallowing, and regulating blood pressure.
By understanding the anatomy and function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that allow us to taste, swallow, and maintain optimal blood pressure.
The Journey of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Now that we have a basic understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve, let us explore the pathway it takes to reach the parotid gland. The parotid gland is one of the major salivary glands, situated in front of and below the ear, and it plays a crucial role in the production and secretion of saliva.
Pathway of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is not merely a solitary traveler on its journey to the parotid gland but rather engages in a series of interactions and connections with other nerves. After leaving the medulla oblongata, the nerve descends alongside the vagus and accessory nerves within the jugular foramen.
Upon exiting the skull, it branches out and forms delicate connections with neighboring nerves, such as the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve and the auriculotemporal nerve from the trigeminal nerve. These interconnections pave the way for the glossopharyngeal nerve to continue its hitchhiking journey towards the parotid gland.
Nerves Interacting with the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The interconnections between the glossopharyngeal nerve and neighboring nerves serve crucial functions. One such interaction occurs via the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, which forms a delicate loop known as Jacobson’s nerve within the middle ear.
This connection is of significance due to the presence of the tympanic plexus, an intricate web of nerves located within the middle ear cavity. The tympanic plexus not only carries sensory information but also houses parasympathetic fibers that regulate the blood flow to the parotid gland. The glossopharyngeal nerve’s hitchhiking interaction with this plexus is crucial for ensuring optimal function of the parotid gland.
As the glossopharyngeal nerve continues its journey, it encounters yet another important interaction, this time with the carotid sinus nerve. The carotid sinus nerve, a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, is responsible for relaying sensory information from the carotid sinus, a specialized area in the carotid artery that monitors blood pressure.
This interaction between the glossopharyngeal nerve and the carotid sinus nerve is vital for maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis. The glossopharyngeal nerve acts as a messenger, transmitting information about blood pressure to the brain, which then initiates appropriate responses to regulate blood pressure and ensure the body’s overall well-being.
Additionally, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a role in the sensation of taste. It carries taste signals from the posterior one-third of the tongue, allowing us to savor the flavors of various foods and beverages.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve has connections with the stylopharyngeus muscle, a muscle involved in swallowing and speech. These connections enable the glossopharyngeal nerve to coordinate the movements of the stylopharyngeus muscle, ensuring efficient swallowing and clear articulation of speech.
In conclusion, the journey of the glossopharyngeal nerve is not a solitary one. It intertwines with various nerves, forming intricate connections that serve crucial functions in the body. From regulating blood flow to the parotid gland, monitoring blood pressure, relaying taste sensations, to coordinating muscle movements, the glossopharyngeal nerve is an essential component of our overall physiological functioning.
The Parotid Gland and its Nervous Connections
Turning our attention to the destination itself, the parotid gland is an essential component of the salivary system. It is responsible for producing saliva, which aids in the digestion process, lubricates the oral cavity, and defends against oral pathogens.
Role of the Parotid Gland
The parotid gland has a vital role in the overall maintenance of oral health and function. By producing saliva, it helps moisten food, enabling easier swallowing and digestion. Moreover, saliva contains antimicrobial enzymes that contribute to the defense against bacterial and fungal pathogens in the oral cavity.
But let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of the parotid gland and its intricate nervous connections.
Nervous Supply to the Parotid Gland
Achieving optimal function of the parotid gland necessitates a well-regulated nervous supply. This is where the hitchhiking phenomenon comes into play, as the glossopharyngeal nerve forms a connection with the tympanic plexus in the middle ear.
Imagine a network of nerves working together like a well-choreographed dance. Within the tympanic plexus, parasympathetic fibers travel alongside the glossopharyngeal nerve and eventually branch off into the lesser petrosal nerve. The lesser petrosal nerve then traverses several intricate pathways, connecting with the otic ganglion. It is within the otic ganglion that the hitchhiking phenomenon reveals itself once more.
Picture this: tiny nerve fibers hitching a ride to reach their destination. The hitchhiking occurs when preganglionic parasympathetic fibers travel via the lesser petrosal nerve and synapse with postganglionic neurons within the otic ganglion. From there, postganglionic fibers continue their journey alongside the auriculotemporal nerve, which is a branch of the trigeminal nerve. Eventually, these fibers reach the parotid gland, supplying it with the necessary neurological signals for saliva production.
Isn’t it amazing how our body’s intricate systems work together to ensure our well-being? The nervous connections to the parotid gland demonstrate the complexity and precision of our physiological processes.
So, the next time you take a bite of food and feel the moistness in your mouth, remember the parotid gland and its fascinating nervous connections, silently working behind the scenes to keep your oral health in check.
The Hitchhiking Phenomenon in the Nervous System
The hitchhiking of the glossopharyngeal nerve to the parotid gland exemplifies the intricate nature of the nervous system. This phenomenon highlights the intricate interplay between different nerves to achieve a specific function, in this case, the regulation of salivary secretion.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the back of the tongue, tonsils, and the parotid gland. It also plays a crucial role in controlling the muscles involved in swallowing and the production of saliva. The parotid gland, on the other hand, is one of the major salivary glands located near the ear. It secretes saliva into the mouth, aiding in the digestion of food and maintaining oral health.
Understanding the hitchhiking phenomenon requires delving into the intricate network of nerves within the human body. Nerves, like highways, connect different parts of the body, allowing for the transmission of signals and the coordination of various bodily functions. The hitchhiking of the glossopharyngeal nerve to the parotid gland showcases the complexity and precision of these nerve interactions.
Understanding Nerve Interactions
The hitchhiking phenomenon is just one example of how nerves interact and collaborate within the human body. Nerve interactions are paramount for the proper functioning of various bodily systems and maintaining homeostasis. Disruptions in these interactions can lead to dysfunction and potentially impact human health.
When it comes to the hitchhiking of the glossopharyngeal nerve, it is essential to consider the broader context of nerve pathways and connections. The glossopharyngeal nerve originates from the medulla oblongata, a vital part of the brainstem responsible for controlling many autonomic functions. From there, it travels down the neck, passing through various structures, including the stylopharyngeus muscle and the carotid sinus, before reaching the parotid gland.
Along its journey, the glossopharyngeal nerve interacts with other cranial nerves, such as the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve. These interactions are crucial for coordinating the complex processes involved in salivary secretion. The vagus nerve, for instance, plays a significant role in regulating the parasympathetic control of the salivary glands, while the accessory nerve contributes to the innervation of the muscles involved in swallowing.
Importance of Nerve Hitchhiking
Although the concept of nerve hitchhiking might sound obscure, it holds immense importance in understanding the complexities of the human body. By comprehending nerve interactions and pathways, medical professionals can better diagnose and treat conditions that affect the cranial nerves, salivary glands, and related structures. It underscores the need for comprehensive anatomical knowledge in guiding medical interventions and promoting patient well-being.
Furthermore, the hitchhiking phenomenon serves as a reminder of the remarkable adaptability and efficiency of the nervous system. The ability of nerves to collaborate and share pathways highlights the intricate mechanisms that allow the body to function harmoniously. It is a testament to the evolutionary brilliance of the human body, showcasing how it has evolved to optimize its resources and ensure the smooth operation of vital processes.
In conclusion, the hitchhiking phenomenon of the glossopharyngeal nerve to the parotid gland is a fascinating example of the complexities of the nervous system. It demonstrates the interconnectedness of different nerves and their crucial role in achieving specific functions. By understanding nerve interactions, medical professionals can gain valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions. The hitchhiking phenomenon serves as a reminder of the remarkable adaptability and efficiency of the human body, showcasing the intricate mechanisms that allow it to function harmoniously.
The Connection between the Glossopharyngeal Nerve and Parotid Gland
The glossopharyngeal nerve, one of the twelve cranial nerves, plays a crucial role in the intricate network of nerves within the human body. This nerve, originating from the medulla oblongata, embarks on a fascinating journey to reach the parotid gland, forming intricate connections with other nerves along the way.
The glossopharyngeal nerve’s pathway involves interactions with neighboring nerves, such as the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve and the auriculotemporal nerve from the trigeminal nerve. These interconnections allow the nerve to navigate through the complex anatomy of the head and neck region, ultimately reaching its destination, the parotid gland.
How the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Reaches the Parotid Gland
The glossopharyngeal nerve’s journey begins within the brainstem, specifically the medulla oblongata. From there, it exits the skull through the jugular foramen, a small opening located at the base of the skull. Once outside the skull, the nerve travels downward, passing through the neck region.
As the glossopharyngeal nerve descends, it encounters the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, which plays a vital role in the regulation of the middle ear. This interaction between the two branches highlights the interconnectedness of the nervous system and the intricate coordination required for various bodily functions.
Continuing its journey, the glossopharyngeal nerve encounters the auriculotemporal nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve. This interaction between the glossopharyngeal nerve and the trigeminal nerve further emphasizes the complex interplay between different cranial nerves, each contributing to specific functions within the head and neck region.
Finally, after traversing through these intricate connections, the glossopharyngeal nerve reaches its destination, the parotid gland. This gland, situated in front of the ear, is responsible for producing saliva and plays a crucial role in the digestive process.
Implications of this Connection for Human Health
The connection between the glossopharyngeal nerve and the parotid gland holds significant implications for human health and well-being. Any disruption or dysfunction in this pathway can lead to various issues, such as impaired salivary secretion or altered taste perception.
Impaired salivary secretion can result in difficulties in chewing and swallowing, leading to nutritional deficiencies and reduced quality of life. Altered taste perception, on the other hand, can affect one’s enjoyment of food and may even contribute to nutritional imbalances.
Recognizing the importance of this connection, it is essential to consult with a medical professional for any concerns related to salivary gland function or taste abnormalities. These healthcare providers possess the expertise to diagnose and provide appropriate guidance, ensuring optimal patient care.
The journey of the glossopharyngeal nerve to the parotid gland serves as a reminder of the marvels of the human body. Its hitchhiking through the intricate network of nerves demonstrates the complexity and interdependence of various bodily functions. Embracing the wonders of the human anatomy and the complexities of the nervous system is an essential step towards fostering a deeper appreciation for our own bodies and encouraging further advancements in medical knowledge.