The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is a vital component of the human nervous system. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of this nerve, including its anatomy, functions, muscles it innervates, and disorders associated with it. Understanding the glossopharyngeal nerve is crucial to gaining insights into its role in human physiology.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
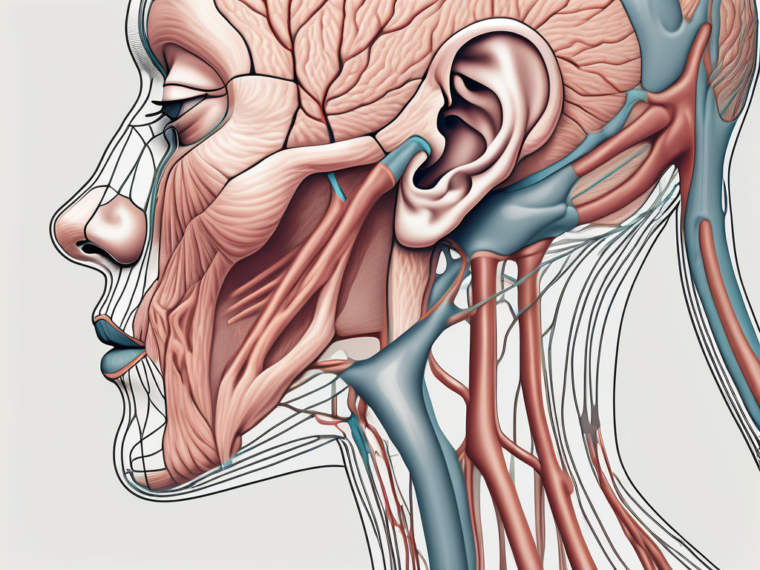
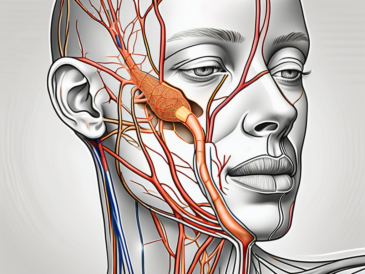
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is a vital component of the human nervous system. It originates from the medulla oblongata, a region located within the brainstem. Emerging from the posterior aspect of the brainstem, this nerve courses downward, branching out to fulfill its various functions.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is primarily composed of sensory and motor fibers, each playing a distinct role in the overall functioning of this nerve. The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate specific areas of the head, including the posterior third of the tongue, the soft palate, and the tonsils. These sensory fibers provide crucial information related to touch, pressure, temperature, and taste sensations from these regions, allowing for a rich sensory experience.
On the other hand, the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve are responsible for the contraction of the stylopharyngeus muscle. This muscle, located in the throat, plays a pivotal role in swallowing and speech production. The coordinated action of the motor fibers ensures smooth and efficient movement of the stylopharyngeus muscle, facilitating these essential functions.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve serves a wide range of functions in the human body, contributing to various physiological processes. One of its essential functions is the facilitation of the gag reflex, a protective mechanism that prevents foreign objects from entering the pharynx. This reflex is crucial for maintaining airway safety and preventing choking incidents, highlighting the vital role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in safeguarding our well-being.
In addition to its role in the gag reflex, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a significant role in the intricate process of swallowing. It aids in coordinating the movement of muscles involved in sequential oral and pharyngeal stages of swallowing, ensuring efficient transportation of food and liquids from the mouth to the esophagus. Without the proper functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve, the process of swallowing would be compromised, leading to difficulties in nutrition intake and overall well-being.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is involved in taste sensation. Together with the facial nerve, it innervates specific taste buds located on the posterior third of the tongue. These taste buds allow us to experience the diverse flavors of the foods we consume, adding pleasure and enjoyment to our meals. Impairment in glossopharyngeal nerve function may lead to alterations or loss of taste perception in affected individuals, impacting their ability to fully appreciate the culinary delights of life.
Overall, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable component of the human nervous system, contributing to various vital functions. Its intricate anatomy and multifaceted role in sensory and motor functions make it an essential part of our daily lives, ensuring the smooth functioning of processes such as swallowing, taste perception, and airway protection.
Muscles Innervated by the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Stylopharyngeus Muscle and its Role
The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in innervating the stylopharyngeus muscle, which is involved in the process of swallowing. The stylopharyngeus muscle aids in elevating the pharynx and larynx during swallowing, facilitating the smooth passage of food and liquids into the esophagus.
Swallowing is a complex and coordinated process that involves the activation of various muscles and nerves. The stylopharyngeus muscle, innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve, is one of the key players in this intricate mechanism. Located in the pharynx, this muscle contracts to elevate and widen the throat, allowing the food or liquid to pass through smoothly.
When you swallow, the tongue pushes the food or liquid to the back of the mouth, triggering a series of muscular contractions. The glossopharyngeal nerve sends signals to the stylopharyngeus muscle, instructing it to contract. As the muscle contracts, it pulls the pharynx and larynx upward and forward, creating a clear pathway for the bolus to travel down the esophagus.
The Interaction between the Glossopharyngeal Nerve and the Stylopharyngeus Muscle
The interaction between the glossopharyngeal nerve and the stylopharyngeus muscle is a delicate interplay that underscores the precision required for swallowing and speech production. Dysfunction or damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can lead to difficulty in swallowing, known as dysphagia, and may necessitate medical intervention and management.
Imagine the intricate coordination required for every swallow you take. The glossopharyngeal nerve, originating from the brainstem, sends signals to the stylopharyngeus muscle, instructing it to contract at the precise moment. This synchronized action ensures that the food or liquid is propelled safely down the esophagus, avoiding any potential complications.
However, disruptions in this delicate interplay can occur. Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve, whether due to trauma, infection, or underlying medical conditions, can result in dysphagia. Dysphagia can manifest as difficulty in initiating a swallow, a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat, or even aspiration, where food or liquid enters the airway instead of the esophagus.
Management of glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction and associated dysphagia may involve a multidisciplinary approach. Speech-language pathologists, neurologists, and otolaryngologists work together to assess and treat the underlying cause of the nerve damage. Rehabilitation techniques, such as swallowing exercises and dietary modifications, may be employed to improve swallowing function and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals affected by glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction.
Disorders Related to the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial cranial nerve that plays a significant role in various functions related to the throat and tongue. When this nerve is damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms and disorders that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Symptoms of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Damage
Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can manifest in various ways, affecting different aspects of throat and tongue function. One common symptom is difficulties in swallowing, also known as dysphagia. This can make it challenging to eat and drink, leading to weight loss and malnutrition if left untreated.
Another symptom of glossopharyngeal nerve damage is a persistent sore throat. This discomfort can be constant or intermittent, making it difficult to find relief. Voice changes may also occur, with individuals experiencing hoarseness or a change in vocal pitch.
Diminished taste perception is another common symptom, as the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in transmitting taste signals from the back of the tongue to the brain. This can lead to a loss of enjoyment in food and beverages, affecting a person’s overall appetite and nutrition.
Pain in the throat or tongue is another symptom that individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve damage may experience. This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe and debilitating, impacting daily activities such as speaking, eating, and even breathing.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis. Only a qualified healthcare provider can provide appropriate guidance and treatment options tailored to your specific condition.
Treatment and Management of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
The treatment and management of glossopharyngeal nerve disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. It is essential to identify and address the root cause of the nerve damage to effectively manage the condition.
A multidisciplinary approach is often necessary when dealing with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders. This may involve consultation with otolaryngologists, neurologists, speech therapists, and other healthcare professionals with expertise in the field.
Treatment options for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders may include medication to manage pain and reduce inflammation. These medications can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall quality of life. Rehabilitation exercises, such as swallowing therapy, may also be recommended to improve swallowing function and prevent complications such as aspiration pneumonia.
In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the glossopharyngeal nerve damage. These procedures aim to repair or remove any obstructions or abnormalities that may be affecting the nerve’s function. It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgery with your healthcare provider before making any decisions.
Throughout the treatment and management process, it is crucial to follow the guidance of healthcare professionals and adhere to their recommendations for optimal outcomes. Regular follow-up appointments and ongoing communication with your healthcare team are essential to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In conclusion, glossopharyngeal nerve disorders can significantly impact a person’s ability to swallow, speak, and enjoy food. Seeking timely medical attention and following the recommended treatment and management strategies are crucial for improving symptoms and enhancing overall quality of life.
The Importance of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Human Body
Role in Swallowing and Speech
The glossopharyngeal nerve’s role in the complex processes of swallowing and speech cannot be understated. Its innervation of the stylopharyngeus muscle enables the precise movement required for swallowing, ensuring the efficient transportation of food and liquids without aspiration or choking.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in coordinating the muscles involved in speech production. It works in conjunction with other cranial nerves to control the movements of the tongue, lips, and vocal cords, allowing us to articulate sounds and communicate effectively.
Without the proper functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve, swallowing and speech would be significantly impaired, leading to difficulties in basic activities such as eating and communicating.
Contribution to Taste Sensation
In addition to its role in swallowing and speech, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a vital role in taste sensation. Working in conjunction with the facial nerve, it significantly influences our ability to perceive taste. These nerves provide the sensory input required to discern various flavors, enhancing our gustatory experiences.
When we savor a delicious meal or enjoy a flavorful beverage, it is the glossopharyngeal nerve that allows us to fully appreciate the intricate combination of sweet, salty, sour, and bitter tastes. Without the proper functioning of this nerve, our ability to enjoy and differentiate between different flavors would be severely compromised.
It is worth noting that taste alterations can also arise from non-neurological factors, such as medication side effects or systemic diseases. In such cases, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of taste disturbances and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a vital component of the human body, contributing to essential functions such as swallowing, speech, and taste sensation. Its intricate network of connections and precise innervation ensure the smooth coordination of these processes, allowing us to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in innervating specific muscles involved in swallowing and speech production. Its sensory function contributes to taste perception, further enhancing our sensory experiences. Understanding and appreciating the complex interplay between the glossopharyngeal nerve and various anatomical structures deepen our comprehension of human physiology.
If you experience any symptoms or concerns related to the glossopharyngeal nerve, it is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management options. Your healthcare professional can guide you through the necessary steps to address any underlying conditions and optimize your overall well-being.