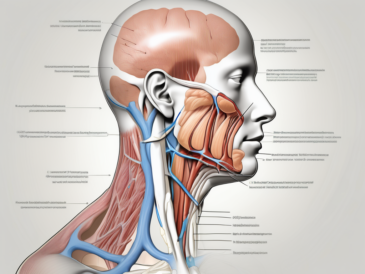
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, plays a critical role in various physiological functions within the human body. It is important to have a comprehensive understanding of this nerve and its functions, as it influences different systems and contributes to overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy and functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve, explore disorders associated with it, discuss methods for diagnosing specific issues, examine available treatment options, and shed light on current research trends and potential breakthroughs in treatment. It is important to note that while this article provides valuable information, it is not intended to replace professional medical advice, and individuals with concerns or symptoms related to the glossopharyngeal nerve should consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is one of the twelve cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem and primarily serving the pharynx and tongue. It is a mixed nerve, meaning that it contains both sensory and motor fibers, as well as autonomic fibers responsible for involuntary functions.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is a fascinating component of the human nervous system. Let’s delve deeper into its anatomy and functions to gain a comprehensive understanding of its role in the body.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve emerges from the medulla oblongata, located within the brainstem. It contains both efferent and afferent fibers, with the efferent fibers involved in controlling certain muscles of the pharynx and the afferent fibers responsible for transmitting sensory information from the tongue, throat, and other structures.
As the glossopharyngeal nerve courses through the skull, it reaches various target regions, exerting its influence on multiple anatomical structures. One of its important destinations is the stylopharyngeus muscle, which aids in swallowing and speech production. This muscle receives motor fibers from the glossopharyngeal nerve, allowing for precise control and coordination during these vital functions.
In addition to its role in the oropharyngeal region, the glossopharyngeal nerve also receives information from the carotid sinus and carotid bodies, which are important in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis. These specialized structures monitor blood pressure and oxygen levels, respectively, and relay this information to the glossopharyngeal nerve for further processing.
The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve provide sensation to the posterior third of the tongue, the tonsils, pharynx, and soft palate. This sensory input is crucial for various activities, such as taste perception and the detection of potential threats or abnormalities in the oropharyngeal region.
The Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Body
The glossopharyngeal nerve serves several functions crucial to the overall functioning of the human body. One of its primary sensory functions is taste perception. The nerve carries taste sensations from the posterior third of the tongue to the brain, allowing individuals to experience the pleasure of eating and drinking. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, the world of flavors would be significantly diminished.
Beyond taste perception, the glossopharyngeal nerve also contributes to swallowing and speech production. The muscles innervated by this nerve help propel food through the pharynx and into the esophagus, ensuring a smooth and efficient swallowing process. In addition, the precise control provided by the glossopharyngeal nerve allows for clear articulation and modulation of speech sounds, enabling effective communication.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a role in regulating blood pressure and heart rate through its interaction with the carotid sinus and carotid bodies. It relays information about blood pressure levels to the brain, allowing the body to respond accordingly and maintain cardiovascular stability. This intricate feedback loop ensures that the heart and blood vessels function optimally, adapting to the body’s needs in different situations.
In summary, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable cranial nerve that contributes to various essential functions in the human body. From taste perception to swallowing, speech production, and cardiovascular regulation, this nerve plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is a vital component of the nervous system. It plays a crucial role in various sensory, motor, and autonomic functions, contributing to the overall well-being of an individual.
Sensory Functions
One of the primary functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve is carrying sensory information from different regions, including the tongue, throat, and tonsils. This sensory input is essential for various physiological processes.
Taste perception is heavily reliant on the glossopharyngeal nerve. It enables us to experience the rich flavors of food and beverages. Without the proper functioning of this nerve, taste sensations can become altered, leading to a diminished enjoyment of eating.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for regulating the gag reflex. This protective mechanism helps prevent choking and aspiration by triggering a reflexive contraction of the throat muscles. Dysfunction of the glossopharyngeal nerve can result in difficulty controlling the gag reflex, potentially compromising airway safety.
In addition to taste and the gag reflex, the glossopharyngeal nerve conveys general sensations from the oropharynx. It allows us to perceive touch, pressure, and temperature in this region. When the nerve is impaired, individuals may experience decreased sensitivity, affecting their ability to detect potential issues or injuries in the affected areas.
Individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction may experience symptoms such as altered taste sensations, difficulty swallowing, and decreased sensitivity in the affected areas. These symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life, making it essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Motor Functions
In addition to its sensory functions, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a crucial role in motor functions related to swallowing and speech production.
The activation of the stylopharyngeus muscle, controlled by the glossopharyngeal nerve, aids in swallowing. This muscle contraction helps propel food and liquids from the mouth to the esophagus, ensuring efficient and safe passage of ingested substances.
Speech production is another motor function influenced by the glossopharyngeal nerve. It assists in the precise movement and coordination of the muscles involved in articulation, allowing for clear and intelligible speech.
Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can result in difficulties in controlling the stylopharyngeus muscle, leading to issues in swallowing and articulation. These challenges can significantly impact an individual’s ability to eat and communicate effectively. Seeking medical attention is crucial in such cases to determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Autonomic Functions
Besides its sensory and motor functions, the glossopharyngeal nerve also carries autonomic fibers responsible for regulating various bodily functions.
Through its connection to the carotid sinus and carotid bodies, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the modulation of blood pressure and heart rate. It plays a role in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis, ensuring that these vital physiological parameters remain within a healthy range.
Disruptions in the autonomic functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve may result in abnormalities in cardiovascular homeostasis. Orthostatic hypotension, a condition characterized by a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing, can occur due to impaired glossopharyngeal nerve function. Other cardiovascular dysregulation issues may also arise, requiring further evaluation and management by healthcare professionals.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a multifaceted cranial nerve with sensory, motor, and autonomic functions. Its proper functioning is crucial for taste perception, regulating the gag reflex, swallowing, speech production, and maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis. Understanding the functions of this nerve helps healthcare professionals diagnose and manage various conditions that may arise from glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction.
Disorders Associated with the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Despite the glossopharyngeal nerve’s importance in multiple functions, disorders specifically targeting this nerve are relatively uncommon. Nevertheless, when they occur, they can have a significant impact on an individual’s well-being and quality of life.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in various sensory and motor functions. It provides innervation to the tongue, throat, and certain glands in the head and neck region. This nerve is responsible for transmitting signals related to taste, swallowing, and speech production.
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition characterized by paroxysmal episodes of severe pain in the area innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve. This rare disorder can be triggered by activities such as swallowing, talking, or coughing, resulting in intense bursts of pain that may last from seconds to minutes.
The exact cause of glossopharyngeal neuralgia is often unknown, but it is believed to be related to irritation or compression of the nerve. In some cases, vascular abnormalities or tumors may contribute to the development of this condition.
Individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of glossopharyngeal neuralgia should consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Treatment may involve medications, nerve blocks, or, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Managing glossopharyngeal neuralgia can be challenging, as the condition can significantly impact a person’s daily activities and overall quality of life. Support from healthcare professionals, pain management strategies, and lifestyle modifications may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and improve well-being.
Damage and Its Effects
Injuries or damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can occur as a result of trauma, infection, or underlying medical conditions. Depending on the extent and location of the damage, individuals may experience various symptoms.
Damage to the sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve can lead to altered taste sensations, reduced sensation in the affected areas, or difficulties in swallowing. This can result in challenges with enjoying food, identifying flavors, or even maintaining proper nutrition.
Motor dysfunction of the nerve may result in problems with muscle control, impacting swallowing and speech production. This can lead to difficulties in communicating effectively and may require speech therapy or other interventions to improve speech and swallowing abilities.
It is essential for individuals experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms to seek medical attention for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and management of glossopharyngeal nerve issues. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help minimize the impact of nerve damage and improve overall functioning.
Diagnosing Glossopharyngeal Nerve Issues
Clinical Examination
Diagnosing glossopharyngeal nerve issues typically involves a comprehensive clinical examination to evaluate the patient’s symptoms and assess their medical history. The healthcare professional may inquire about any specific triggers, the duration and frequency of symptoms, and the impact on the individual’s daily life.
During the examination, the healthcare professional will also assess the individual’s ability to swallow and speak, as well as perform a detailed assessment of the sensory function in the oropharyngeal region.
The clinical examination may involve various tests to evaluate the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve. One common test is the gag reflex test, which assesses the reflexive contraction of the muscles in the back of the throat when the back of the tongue or the pharynx is stimulated. Another test that may be performed is the swallowing test, where the individual is asked to swallow different substances of varying consistencies to assess any difficulties or abnormalities.
Furthermore, the healthcare professional may perform a thorough neurological examination to evaluate other cranial nerves and assess for any associated neurological deficits. This can help determine if the glossopharyngeal nerve issues are isolated or part of a broader neurological condition.
Imaging Techniques
In some cases, imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be used to visualize the glossopharyngeal nerve and surrounding structures. These imaging modalities provide valuable information and can help identify any structural abnormalities or signs of damage that may be contributing to the symptoms.
During an MRI or CT scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, tunnel-like machine. The machine uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the internal structures. These images can help healthcare professionals visualize the glossopharyngeal nerve, nearby blood vessels, and any potential tumors, lesions, or other abnormalities that may be affecting the nerve’s function.
Additionally, specialized imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or magnetic resonance venography (MRV) may be used to specifically evaluate the blood vessels in the area. This can be particularly useful in cases where vascular compression or abnormalities are suspected as a cause of glossopharyngeal nerve issues.
It is important to note that while imaging techniques can provide valuable information, they are typically used in conjunction with the clinical examination and medical history to make an accurate diagnosis. The healthcare professional will consider all the available information to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for the individual.
Treatment Options for Glossopharyngeal Nerve Disorders
Glossopharyngeal nerve disorders, such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, can cause severe pain and discomfort. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to help manage these conditions and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Medication and Non-Surgical Treatments
When it comes to treating glossopharyngeal nerve-related disorders, the initial approach often involves medication and non-surgical interventions. Medications can be prescribed to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and manage associated symptoms.
Non-surgical treatments may also be recommended, depending on the specific symptoms and their impact on the individual’s well-being. Nerve blocks, which involve injecting an anesthetic near the affected nerve, can provide temporary relief. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may also be beneficial in improving muscle strength and coordination, as well as reducing pain and discomfort.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Each person’s circumstances may vary, and a personalized approach can help optimize outcomes. The healthcare provider will take into account factors such as the severity of symptoms, the individual’s overall health, and any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the glossopharyngeal nerve disorder.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatment options fail to adequately alleviate symptoms or when structural abnormalities contribute to the glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction, surgical interventions may be considered. These procedures aim to relieve symptoms and restore optimal function.
One surgical procedure that may be performed is microvascular decompression. This involves repositioning blood vessels that may be compressing the glossopharyngeal nerve, thereby relieving pressure and reducing symptoms. Another option is radiofrequency ablation, which uses heat generated by radio waves to target and destroy the nerve fibers responsible for transmitting pain signals. Percutaneous nerve block techniques, where medication is injected directly into the affected nerve, can also be utilized to provide relief.
However, the decision to pursue surgical interventions should be based on a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. They will consider the individual’s symptoms, overall health, and potential risks and benefits associated with the procedure. Surgical interventions are typically reserved for cases where other treatment options have been unsuccessful or when there is a clear structural issue contributing to the glossopharyngeal nerve disorder.
In conclusion, treatment options for glossopharyngeal nerve disorders range from medication and non-surgical interventions to surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s specific circumstances and should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. With the right approach, it is possible to manage symptoms, reduce pain, and improve the overall well-being of those affected by glossopharyngeal nerve disorders.
The Future of Glossopharyngeal Nerve Research
Current Research Trends
Glossopharyngeal nerve research continues to evolve, focusing on emerging techniques and therapeutic approaches for the management of glossopharyngeal neuralgia and other related disorders. Efforts are underway to refine diagnostic tools, improve treatment modalities, and enhance our understanding of the underlying mechanisms.
Ongoing research also explores the potential impact of neuromodulation techniques, such as deep brain stimulation or peripheral nerve stimulation, in managing glossopharyngeal nerve-related conditions. These innovative approaches hold promise for more targeted and efficient interventions.
Potential Breakthroughs in Treatment
As research in the field progresses, potential breakthroughs in the treatment of glossopharyngeal nerve disorders may emerge. These breakthroughs could include novel medications, advancements in surgical techniques, or innovative approaches utilizing emerging technologies.
With a better understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and advancements in medical science, individuals suffering from glossopharyngeal nerve-related conditions may benefit from more effective and personalized treatment options in the future.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in numerous functions within the human body, encompassing sensory, motor, and autonomic aspects. Disorders associated with this nerve, although relatively rare, can significantly impact an individual’s well-being. Proper diagnosis, evaluation, and management by healthcare professionals are crucial for optimizing outcomes. Ongoing research aims to further enhance our understanding of glossopharyngeal nerve-related conditions and explore innovative treatment options. While this article provides valuable insights, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for tailored advice and recommendations based on individual circumstances.