Discover the fascinating role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in transmitting parasympathetic axons.
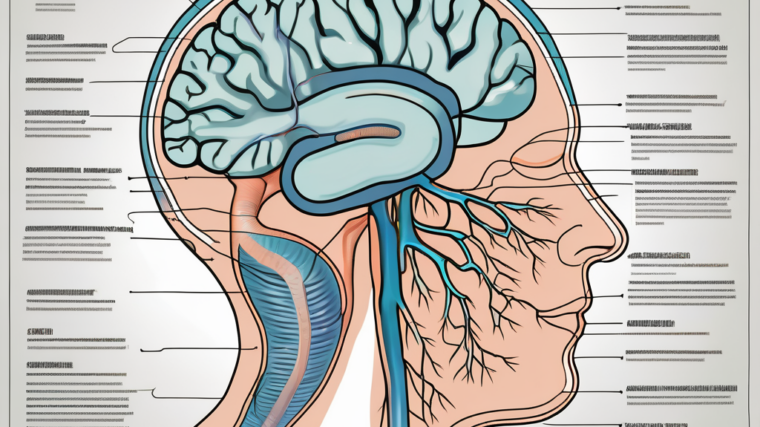

Discover the fascinating role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in transmitting parasympathetic axons.
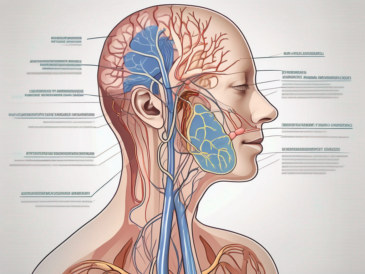
Explore the intricate network of anatomical structures innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
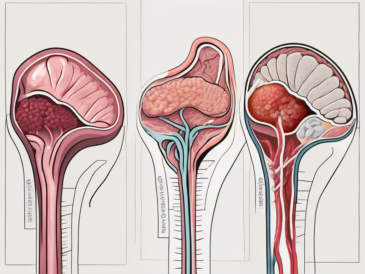
Discover the fascinating impact of a damaged glossopharyngeal nerve on your ability to taste.
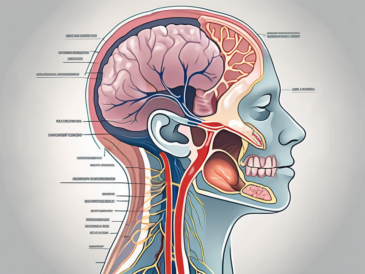
Discover the intricate network of muscles controlled by the glossopharyngeal nerve in this comprehensive article.
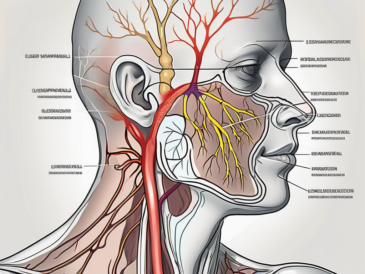
Discover the underlying factors that can lead to dysfunction of the glossopharyngeal nerve in this comprehensive article.
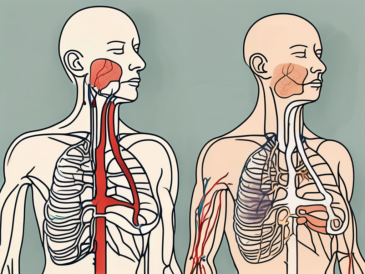
Learn how to recognize potential issues with the glossopharyngeal nerve in this comprehensive article.
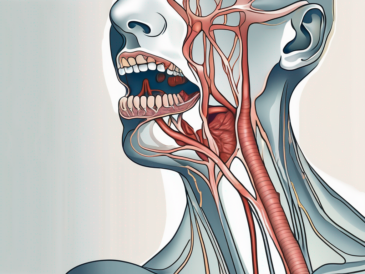
Discover the fascinating functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve in this comprehensive article.
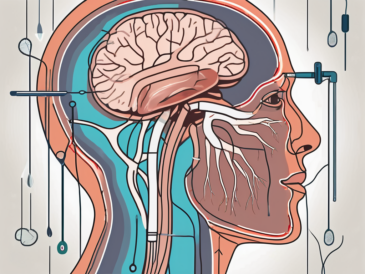
Discover the various tests that can be used to assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve in this comprehensive article.
Learn about the fascinating connection between the glossopharyngeal nerve and a specific lobe of the brain.
Discover the fascinating role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in controlling crucial functions such as swallowing, taste sensation, and even blood pressure regulation.