Testing the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves is an essential part of evaluating various neurological disorders and conditions. These nerves play crucial roles in the body, and understanding how to test them can aid in diagnosing and managing related issues effectively. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves, explain their roles in the body, discuss the importance of nerve testing, and provide guidelines for conducting the tests, interpreting results, and managing potential complications.
Understanding the Hypoglossal and Glossopharyngeal Nerves
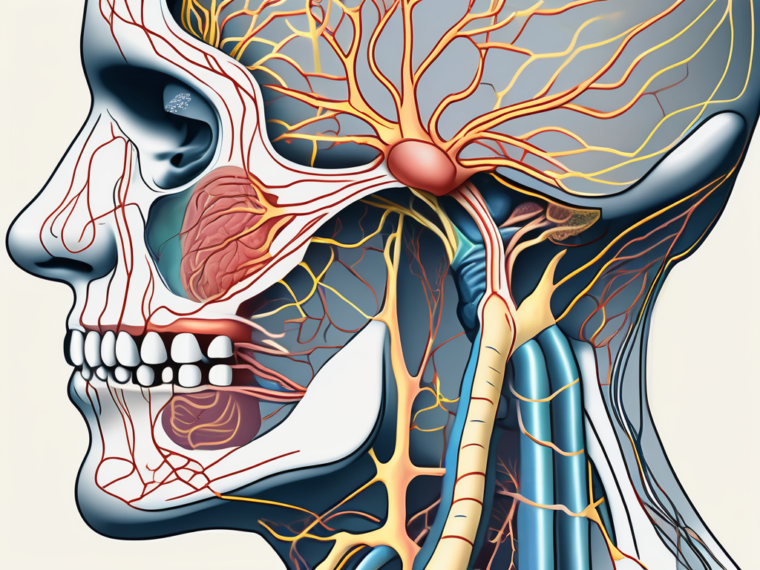
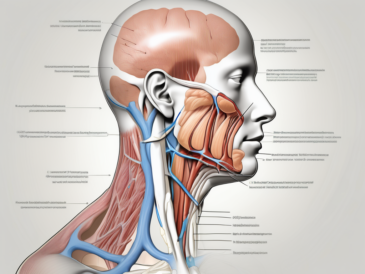
The human body is a complex system of interconnected parts, and the nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating and controlling various functions. Two important components of the nervous system are the hypoglossal nerve and the glossopharyngeal nerve. Let’s delve deeper into the anatomy of these nerves to gain a better understanding of their functions and significance.
Anatomy of the Hypoglossal Nerve
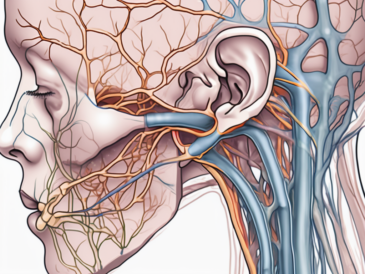
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as cranial nerve XII, is a vital component of the nervous system responsible for innervating the muscles of the tongue. This nerve originates in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, which is located at the base of the brain. From its origin, the hypoglossal nerve travels through specific pathways, including the hypoglossal canal, to reach its intended muscles.
Upon reaching the tongue, the hypoglossal nerve branches out extensively, supplying motor fibers to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue. These muscles play a crucial role in various functions, such as swallowing, speech, and chewing. The hypoglossal nerve ensures the precise coordination and movement of these muscles, allowing for the intricate control required for these activities.
Understanding the precise anatomy of the hypoglossal nerve is crucial for accurate testing and interpretation of results. Nerve testing, such as electromyography, can help evaluate the function of the hypoglossal nerve and diagnose any potential abnormalities or conditions that may affect its proper functioning.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve, or cranial nerve IX, is another essential component of the nervous system. It is responsible for providing sensory, motor, and autonomic innervation to various structures, including the throat, tongue, and salivary glands.
Similar to the hypoglossal nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve originates in the medulla oblongata. From there, it travels through specific pathways, including the jugular foramen, to reach its target structures. The glossopharyngeal nerve carries sensory information from the back of the throat, the base of the tongue, and the tonsils, allowing for the perception of taste, touch, and pain in these areas.
In addition to its sensory function, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a role in motor control, specifically in the muscles involved in swallowing and speech production. Furthermore, it provides autonomic innervation to the parotid salivary gland, regulating its secretory function.
Familiarity with the anatomy of the glossopharyngeal nerve is vital for successful nerve testing and evaluation. Various diagnostic procedures, such as a glossopharyngeal nerve block, can help determine the source of pain or dysfunction in the structures innervated by this nerve.
As we can see, the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves are intricate components of the nervous system, each with its own unique functions and anatomical pathways. Understanding their anatomy is crucial for accurate testing, diagnosis, and treatment of any potential issues that may arise. The complexity of these nerves highlights the remarkable intricacies of the human body and the importance of the nervous system in maintaining its proper functioning.
The Importance of Nerve Testing
Nerve testing, also known as nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG), is a valuable diagnostic tool used to assess the function and integrity of nerves. It plays a crucial role in the field of healthcare by providing healthcare professionals with essential information to guide them in determining appropriate courses of treatment. By evaluating the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves, nerve testing helps identify potential abnormalities and allows for early intervention and management of various conditions.
Role of the Hypoglossal Nerve in the Body
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, primarily controls the movement and strength of the tongue muscles. This nerve is responsible for ensuring proper speech, chewing, swallowing, and tongue movements. It plays a vital role in our daily lives, allowing us to communicate effectively and consume food and liquids without difficulty.
During nerve testing, healthcare professionals assess the function of the hypoglossal nerve by measuring the electrical signals transmitted through it. By analyzing the conduction velocity and amplitude of these signals, they can identify any disruptions or impairments affecting the critical functions controlled by the hypoglossal nerve.
Abnormalities in the hypoglossal nerve can have significant consequences on a person’s quality of life. Conditions such as hypoglossal nerve palsy, which occurs when the nerve is damaged or compressed, can lead to difficulties in speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Nerve testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing these conditions and guiding healthcare professionals in developing appropriate treatment plans.
Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Body
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, contributes to various essential functions in the body. It provides sensory input to the back of the throat, taste perception from the posterior third of the tongue, and controls certain muscles involved in swallowing.
Testing the glossopharyngeal nerve is essential in identifying abnormalities that may lead to swallowing difficulties, speech issues, or abnormalities in taste perception. By assessing the conduction of electrical signals through this nerve, healthcare professionals can detect any disruptions or impairments that may affect its function.
Swallowing difficulties, known as dysphagia, can significantly impact a person’s ability to eat and drink safely. It can lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia. Nerve testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing the underlying causes of dysphagia, including glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction, and guiding healthcare professionals in developing appropriate treatment strategies.
Furthermore, abnormalities in the glossopharyngeal nerve can also affect taste perception. The posterior third of the tongue, innervated by this nerve, is responsible for detecting certain tastes, such as bitter and sour. Any disruptions in the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve can result in altered taste perception, affecting a person’s enjoyment of food and potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies.
In conclusion, nerve testing, including the evaluation of the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves, plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing various conditions that affect speech, swallowing, and taste perception. By providing healthcare professionals with valuable information about the function and integrity of these nerves, nerve testing enables early intervention and appropriate treatment planning, ultimately improving patients’ quality of life.
Preparing for the Nerve Test
When it comes to conducting a nerve test, there are several important steps to take to ensure accurate and reliable results. One of the first things to consider is gathering the necessary equipment. This typically includes an EMG machine, surface electrodes, a nerve stimulator, and appropriate cleaning agents to maintain proper hygiene throughout the process. Each piece of equipment plays a crucial role in the overall test, so it is important to ensure that everything is in good working order before proceeding.
Once the equipment is ready, the next step is to prepare the patient for the nerve test. This involves providing them with clear and concise instructions on what to expect and how to prepare. For example, patients may be advised to abstain from consuming caffeine, nicotine, and certain medications that could potentially interfere with the test results. These substances have the potential to affect nerve conduction and could lead to inaccurate readings.
Furthermore, explaining the purpose and potential benefits of the nerve test to the patient can help alleviate any anxiety or concerns they may have. It is important for patients to understand that this test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable insights into their nerve function. By explaining the significance of the test, patients are more likely to feel comfortable and confident throughout the process.
Additionally, it is crucial to address any questions or concerns the patient may have prior to the test. This can help establish trust and rapport between the patient and the healthcare professional conducting the test. By taking the time to listen and address any concerns, patients will feel more at ease and confident in the procedure.
Overall, preparing for a nerve test involves both gathering the necessary equipment and ensuring that the patient is well-informed and prepared. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate and reliable test results while providing a positive and comfortable experience for the patient.
Conducting the Hypoglossal Nerve Test
The hypoglossal nerve test is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the function and integrity of the hypoglossal nerve. This nerve plays a crucial role in controlling the movement of the tongue muscles, allowing for proper speech and swallowing. By stimulating the nerve with an electric current and recording the resulting muscle responses, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the nerve’s health.
Step-by-Step Procedure
The hypoglossal nerve test typically involves several steps to ensure accurate and reliable results. The procedure begins with the placement of surface electrodes on the tongue muscles while the patient is at rest. These electrodes are designed to detect and record the electrical activity generated by the muscles.
Once the electrodes are in place, a nerve stimulator is used to deliver controlled electrical impulses to the hypoglossal nerve. This stimulation triggers contractions in the relevant tongue muscles, which are then detected and recorded by the electrodes. The electrical activity is converted into visual or auditory signals, allowing healthcare professionals to analyze the responses.
During the test, the patient may be asked to perform specific tasks, such as sticking out their tongue or moving it from side to side. These movements help assess the nerve’s ability to control the tongue muscles and provide additional information about its functionality.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the results of the hypoglossal nerve test requires expertise and experience. Healthcare professionals trained in neurophysiology or neurology are typically responsible for analyzing the data and drawing conclusions.
Abnormalities in the muscle responses recorded during the test may indicate various conditions affecting the hypoglossal nerve. Nerve damage, motor neuron disorders, or certain systemic conditions can all lead to abnormal responses. However, it is important to note that abnormal results do not necessarily confirm a specific diagnosis. Further evaluation and consideration of other clinical information are essential to form an accurate diagnosis and determine appropriate treatment options.
Consulting a healthcare professional experienced in interpreting nerve test results is advisable to ensure a comprehensive analysis and appropriate follow-up. They can provide valuable insights and guide patients through the diagnostic process, helping them understand the implications of the test results and the next steps in their healthcare journey.
Conducting the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
The glossopharyngeal nerve test is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the function and integrity of the glossopharyngeal nerve. This nerve plays a crucial role in various functions, including swallowing, throat sensation, and taste perception. By conducting this test, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the health of this important nerve.
Step-by-Step Procedure
When performing the glossopharyngeal nerve test, healthcare professionals follow a step-by-step procedure to ensure accurate and reliable results. The procedure involves the use of surface electrodes and a nerve stimulator to elicit specific responses from the relevant muscles.
First, the patient is positioned comfortably, typically sitting or lying down. The healthcare professional then places surface electrodes on the muscles associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve, such as the muscles of the throat and tongue. These electrodes are used to measure the electrical activity of the muscles during the test.
Once the electrodes are in place, the nerve stimulator is used to deliver controlled electrical impulses to the glossopharyngeal nerve. These impulses stimulate the nerve and elicit specific responses in the muscles being tested. The healthcare professional carefully monitors and records these responses throughout the test.
During the test, the patient may be asked to perform certain actions, such as swallowing or sticking out their tongue, to further assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve. These actions help to evaluate the coordination and strength of the muscles associated with the nerve.
Throughout the procedure, the healthcare professional ensures the patient’s safety and comfort. They also take note of any discomfort or adverse reactions experienced by the patient during the test.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the results of the glossopharyngeal nerve test requires a thorough analysis of the muscle responses and their correlation with clinical findings. Abnormalities in the responses may indicate underlying issues with swallowing, throat sensation, or taste perception.
Healthcare professionals experienced in analyzing nerve test results play a crucial role in interpreting the findings. They carefully review the data collected during the test and consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic tests to make an accurate assessment.
Based on the results, the healthcare professional can provide valuable insights into potential diagnoses and management strategies. They may recommend further tests or consultations with specialists to determine the underlying cause of any abnormalities detected during the glossopharyngeal nerve test.
It is important to note that the glossopharyngeal nerve test is just one tool in the diagnostic process. It is typically performed in conjunction with other tests and evaluations to provide a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve test is a valuable procedure used to evaluate the function and integrity of the glossopharyngeal nerve. By following a step-by-step procedure and interpreting the results accurately, healthcare professionals can gather important information about the health of this vital nerve and guide appropriate management strategies.
Potential Complications and Risks
When it comes to hypoglossal nerve testing, it is generally considered a safe procedure. However, as with any medical test, there are a few potential risks and complications that may arise. It is important to be aware of these possibilities and address any concerns that patients may have.
Risks Associated with Hypoglossal Nerve Testing
One potential risk is the experience of minor discomfort during the procedure. While this discomfort is usually temporary and manageable, it is important for patients to be prepared for this possibility. The healthcare provider performing the test will take steps to minimize any discomfort, but it is important for patients to communicate any concerns or discomfort they may experience.
In addition to discomfort, some patients may experience muscle soreness after the test. This is a common side effect and is typically temporary. It is important for patients to rest and take care of themselves following the test, allowing their muscles to recover.
Another potential risk associated with hypoglossal nerve testing is the rare chance of infection. This risk can be minimized by ensuring that proper hygiene practices are upheld during the procedure. Healthcare providers should follow strict protocols to prevent infection, such as using sterile equipment and maintaining a clean environment. Patients should also be informed of the importance of maintaining good hygiene, both before and after the test, to further reduce the risk of infection.
It is crucial for healthcare providers to inform patients of these potential risks associated with hypoglossal nerve testing. By providing patients with this information, they can make informed decisions and have a clear understanding of what to expect during and after the test.
Risks Associated with Glossopharyngeal Nerve Testing
Glossopharyngeal nerve testing shares similar risks to that of hypoglossal nerve testing. Patients may experience minimal discomfort during the procedure, which is usually temporary and manageable. It is important for healthcare providers to communicate this possibility to patients, ensuring they are prepared and informed.
Like with hypoglossal nerve testing, patients may also experience muscle soreness after glossopharyngeal nerve testing. This is a common side effect and is typically temporary. Patients should be advised to rest and take care of themselves following the test, allowing their muscles to recover.
Similarly, there is a rare chance of infection associated with glossopharyngeal nerve testing if proper hygiene practices are not followed. Healthcare providers should adhere to strict hygiene protocols to minimize this risk. Patients should also be educated on the importance of maintaining good hygiene before and after the test to further reduce the risk of infection.
It is essential for healthcare providers to inform patients of these potential risks associated with glossopharyngeal nerve testing. By doing so, patients can make informed decisions and have a clear understanding of the possible complications that may arise.
Post-Test Procedures and Follow-up
What to Expect After the Test
Following the nerve testing procedure, patients may experience mild muscle soreness or fatigue. It is important to inform patients that these symptoms are generally temporary and should subside within a few days. However, if symptoms worsen or persist, patients should be advised to seek medical attention.
Importance of Follow-up Appointments
After the nerve testing, healthcare professionals may recommend follow-up appointments to discuss the test results, provide further guidance, and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Communicating with a healthcare professional is essential for understanding the test results and addressing any concerns or questions that may arise.
In conclusion, testing the hypoglossal and glossopharyngeal nerves is crucial for assessing various neurological conditions and disorders. By understanding the anatomy, roles, and importance of these nerves, healthcare professionals can conduct nerve tests effectively, interpret results accurately, and manage potential complications. It is imperative to prioritize patient comfort and safety throughout the testing process and encourage ongoing communication with trusted healthcare professionals for comprehensive care and support.