The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial cranial nerve responsible for various functions related to taste, swallowing, and sensation in the ear. Testing the glossopharyngeal nerve during an exam is an essential diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess its proper functioning. In this article, we will discuss the anatomy and functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve, the necessary preparations for the test, a step-by-step guide to performing the examination, how to interpret the results, safety measures to be taken, and answer frequently asked questions about glossopharyngeal nerve testing.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
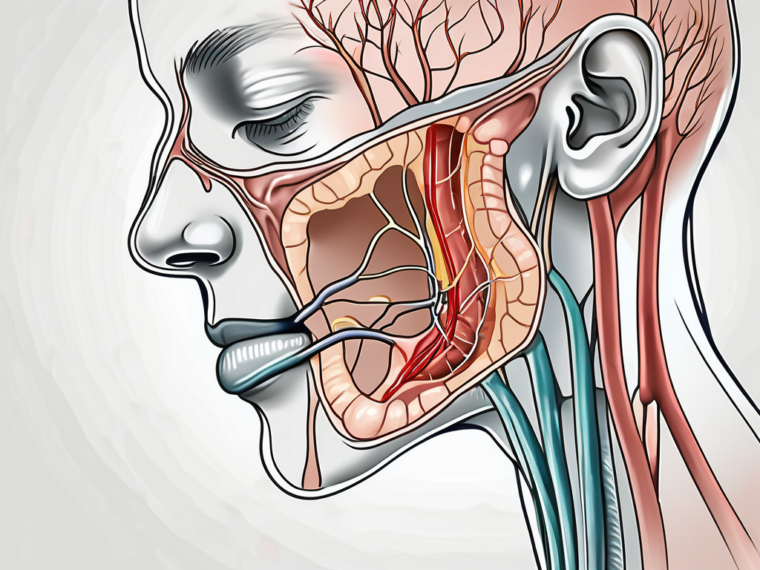
Before delving into the testing procedures, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve. This nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is one of the twelve cranial nerves present in the human body. It arises from the medulla oblongata, the lowermost part of the brainstem, and carries sensory and motor fibers to different structures of the head and neck region.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a fascinating and complex component of the nervous system. It originates from the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for controlling various vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. This nerve plays a crucial role in connecting the brain to the tongue, pharynx, and other important structures in the head and neck.
The glossopharyngeal nerve consists of both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers of the nerve provide taste sensation to the posterior third of the tongue, monitor blood pressure, and carry sensory signals from the pharynx, tonsils, and middle ear. These sensory functions are essential for our ability to enjoy the taste of food, maintain proper blood pressure levels, and perceive sensations in our throat and ears.
On the other hand, the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve innervate the stylopharyngeus muscle, which is responsible for elevating the pharynx during swallowing. This muscle contraction is vital for the smooth movement of food from the mouth to the esophagus, ensuring efficient digestion and preventing choking or aspiration.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a complex structure that traverses through various regions of the head and neck. It emerges from the medulla oblongata and passes through the jugular foramen, a small opening located at the base of the skull. From there, it branches out into different directions, reaching its target structures.
One of the main branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for providing taste sensation to the posterior third of the tongue. This allows us to savor the flavors of different foods and beverages, enhancing our overall dining experience. The nerve fibers responsible for taste perception are intricately connected to taste buds on the tongue, transmitting signals to the brain for interpretation.
In addition to taste sensation, the glossopharyngeal nerve also carries sensory signals from the pharynx, tonsils, and middle ear. These signals play a crucial role in our ability to swallow, detect potential infections or abnormalities in the throat, and maintain proper balance and hearing. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, our ability to perceive these sensations would be greatly compromised.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve performs various functions that are essential for proper oral and pharyngeal functionality. It plays a vital role in taste perception, allowing us to differentiate between different flavors and textures. Imagine not being able to taste the sweetness of a ripe strawberry or the tanginess of a lemon!
Additionally, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the gag reflex, a protective mechanism that prevents foreign objects from entering the throat. This reflex is triggered when the back of the throat is stimulated, causing a contraction of the pharyngeal muscles and a sensation of choking. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, our ability to protect our airway from potential dangers would be compromised.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve facilitates the regulation of blood pressure by providing sensory input to important receptors in the carotid arteries. These receptors, known as baroreceptors, detect changes in blood pressure and send signals to the brain for appropriate adjustments. The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in this feedback loop, ensuring that our blood pressure remains within a healthy range.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable component of the human nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and diverse functions contribute to our ability to taste, swallow, protect our airway, and regulate blood pressure. Understanding the complexities of this nerve is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as it enables us to appreciate the wonders of the human body.
Preparing for the Examination
Conducting a thorough examination of the glossopharyngeal nerve requires appropriate preparation to ensure accurate results. The following factors should be considered:
Necessary Equipment for the Test
Prior to performing the glossopharyngeal nerve test, healthcare professionals must gather the necessary equipment. This typically includes a depressor or tongue blade, a cotton swab, a cup with water, and a light source for adequate visualization of the oropharynx.
When it comes to the depressor or tongue blade, it is important to choose a suitable size and shape. The healthcare professional should ensure that the depressor is clean and sterile before use, as any contamination can affect the accuracy of the test results. Additionally, the cotton swab should be fresh and free from any substances that could interfere with taste perception.
The cup with water serves multiple purposes during the examination. It can be used to rinse the patient’s mouth before and after the test, ensuring a clean environment for accurate assessment. The water can also be used to moisten the cotton swab, facilitating the stimulation of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Furthermore, a reliable light source is essential for proper visualization of the oropharynx. This can be achieved using a handheld otoscope or a headlamp with a bright and focused beam. The healthcare professional should ensure that the light source is functioning optimally, as any dimness or inconsistency in the light can hinder the examination process.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
Instructing the patient about the test and ensuring their cooperation is crucial for a successful examination. Before the test, patients should be advised to refrain from eating or drinking for a specific period to prevent interference with taste perception.
It is important to explain to the patient the purpose of the examination and what they can expect during the process. This helps alleviate any anxiety or apprehension they may have. Clear communication is key, as it allows the patient to understand the importance of their cooperation and follow any instructions given by the healthcare professional.
During the pre-examination discussion, the healthcare professional should also inquire about any relevant medical history or medications the patient may be taking. Certain conditions or medications can affect the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, and being aware of these factors can help interpret the test results accurately.
Addressing any concerns or questions the patient might have is crucial for their comfort and cooperation. The healthcare professional should create a supportive and empathetic environment, ensuring that the patient feels heard and understood. This can help build trust and enhance the overall examination experience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Performing a thorough assessment of the glossopharyngeal nerve involves a systematic approach that includes various steps. The following is a step-by-step guide:
Initial Assessment
Healthcare professionals begin by obtaining the patient’s medical history, including any relevant symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, altered taste sensation, or episodes of dizziness. This information helps in establishing a baseline for the examination.
During the initial assessment, the healthcare professional may also inquire about any recent infections or injuries that could potentially affect the glossopharyngeal nerve. Understanding the patient’s overall health and medical background is crucial in identifying potential underlying causes of glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction.
Additionally, the healthcare professional may perform a physical examination to assess the patient’s overall cranial nerve function. This may involve checking for any abnormalities in the patient’s facial muscles, eye movements, and coordination.
Performing the Gag Reflex Test
The gag reflex test is a vital component of glossopharyngeal nerve testing. It involves gently stimulating the posterior pharyngeal wall with a tongue depressor or cotton swab. A normal response is the contraction of the muscles in the throat, leading to a reflexive gagging. Impaired or absent gag reflex may indicate glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction.
During the gag reflex test, the healthcare professional may also observe the patient’s ability to swallow saliva or water. Difficulties in swallowing or a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat can be indicative of glossopharyngeal nerve impairment.
In some cases, additional diagnostic tests such as imaging studies or electromyography (EMG) may be recommended to further evaluate the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Evaluating Taste Sensation
Assessing taste sensation is another important aspect of the glossopharyngeal nerve examination. This can be done by applying various taste stimuli, such as sweet, sour, salty, or bitter substances, to different regions of the patient’s tongue. The patient should be able to identify and differentiate between these tastes. Abnormal taste perception could indicate glossopharyngeal nerve impairment.
During the evaluation of taste sensation, the healthcare professional may also assess the patient’s ability to detect subtle changes in taste intensity. This can be done by presenting the patient with different concentrations of taste stimuli and asking them to identify the differences.
Furthermore, the healthcare professional may examine the patient’s ability to taste specific flavors that are associated with certain regions of the tongue. For example, the back of the tongue is typically responsible for detecting bitter tastes, while the sides of the tongue are more sensitive to sour tastes.
It is important to note that taste perception can be influenced by various factors, such as medications, smoking, or certain medical conditions. Therefore, the healthcare professional must consider these factors when interpreting the results of the taste sensation evaluation.
By following this step-by-step guide, healthcare professionals can effectively assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve and identify any potential abnormalities or dysfunctions. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the results of the glossopharyngeal nerve test requires a comprehensive understanding of the expected outcomes and potential abnormalities.
The glossopharyngeal nerve test is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, which is responsible for various important functions in the throat and tongue. This nerve plays a crucial role in the gag reflex, taste sensation, and swallowing. By evaluating the responses of the patient during the test, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the health of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
During the test, the healthcare provider will stimulate the glossopharyngeal nerve by applying different taste stimuli to the patient’s tongue and assessing their responses. The patient will be asked to differentiate between various tastes, such as sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. Additionally, the healthcare provider will check the patient’s gag reflex by touching the back of their throat with a tongue depressor or a cotton swab.
Normal Test Results
In a normal glossopharyngeal nerve examination, the patient should demonstrate an intact gag reflex and accurately differentiate between different taste stimuli. A healthy glossopharyngeal nerve allows the patient to perceive and distinguish various tastes accurately. Furthermore, the patient should not report any symptoms like difficulty swallowing or altered taste sensation.
When the glossopharyngeal nerve is functioning properly, the patient’s gag reflex will be triggered appropriately when the back of the throat is stimulated. This reflex helps protect the airway by preventing foreign objects from entering the respiratory system. Moreover, the patient will be able to identify and describe the different tastes presented during the test, indicating that the nerve is transmitting taste signals effectively to the brain.
Abnormal Test Results and Potential Causes
Abnormal test results may indicate various underlying conditions affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve. These abnormalities can be caused by a range of factors, including glossopharyngeal neuralgia, infections, tumor compressions, or other neurological disorders.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition characterized by severe pain in the throat, tongue, and ear, which can be triggered by swallowing, speaking, or even touching the affected areas. This condition can result in abnormal glossopharyngeal nerve test results, as the nerve may be irritated or compressed, leading to altered sensory responses.
Infections, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis, can also affect the glossopharyngeal nerve and cause abnormal test results. The inflammation and swelling associated with these infections can disrupt the normal functioning of the nerve and affect the patient’s ability to swallow and perceive tastes accurately.
Tumor compressions on the glossopharyngeal nerve can also lead to abnormal test results. Tumors can exert pressure on the nerve, interfering with its ability to transmit signals properly. This can result in a compromised gag reflex and altered taste sensation.
Other neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or stroke, can affect the glossopharyngeal nerve and produce abnormal test results. These conditions can cause damage to the nerve fibers, leading to impaired function.
When abnormal test results are obtained, it is crucial to further investigate the underlying cause. Additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction tests, may be necessary to determine the precise cause of the abnormal results. Once the cause is identified, appropriate management can be initiated to address the underlying condition and alleviate symptoms.
Safety Measures and Precautions
During the glossopharyngeal nerve examination, healthcare professionals must prioritize patient safety and take necessary precautions to minimize risks.
When performing a glossopharyngeal nerve examination, it is essential to create a safe environment for both the healthcare professional and the patient. This involves ensuring that the examination room is clean and well-equipped with all the necessary tools and equipment. The healthcare professional should also wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and a face mask, to prevent the spread of infections and maintain a sterile environment.
One of the primary risks associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve examination is discomfort. The procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into the patient’s throat, which can cause a gag reflex and temporary discomfort. To minimize this risk, healthcare professionals should be gentle and use a lubricant to make the insertion smoother. They should also communicate with the patient throughout the procedure, encouraging them to relax and breathe deeply to reduce the likelihood of a gag reflex.
In some cases, the gag reflex can induce vomiting, which can be unpleasant for both the patient and the healthcare professional. To prevent this, it is crucial to ensure that the patient has an empty stomach before the examination. This can be achieved by instructing the patient to refrain from eating or drinking for a specific period before the procedure. Additionally, having a suction device readily available in the examination room can quickly and effectively remove any vomit, if necessary.
Risks Associated with the Test
The glossopharyngeal nerve examination is generally safe; however, there are certain risks associated with the procedure. These risks primarily include discomfort, gag reflex-induced vomiting, or rare incidences of bleeding or infection. Careful adherence to proper technique and the use of sterile equipment can help mitigate these risks.
While the risks of bleeding or infection during a glossopharyngeal nerve examination are rare, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant and take appropriate measures to prevent such complications. This includes ensuring that all equipment used during the procedure is sterile and properly cleaned. The healthcare professional should also have a thorough understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the glossopharyngeal nerve to minimize the risk of accidental injury.
Ensuring Patient Comfort and Safety
Ensuring patient comfort during the glossopharyngeal nerve examination is crucial. Healthcare professionals should maintain open communication with the patient, explain the procedure thoroughly, and address any anxieties or concerns. Additionally, following appropriate infection control measures and practicing hygiene guidelines will help ensure patient safety.
Prior to the examination, healthcare professionals should take the time to explain the procedure to the patient in detail. This includes discussing the purpose of the examination, what to expect during the procedure, and any potential risks or complications. By providing this information, patients can make informed decisions and feel more at ease throughout the examination.
During the examination, healthcare professionals should continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs and response to the procedure. This includes checking their heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels. Any signs of distress or discomfort should be promptly addressed to ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve examination is a safe procedure when performed by trained healthcare professionals. By prioritizing patient safety, adhering to proper technique, and maintaining open communication with the patient, the risks associated with the examination can be minimized.
Frequently Asked Questions about Glossopharyngeal Nerve Testing
How Often Should the Test be Conducted?
The frequency of glossopharyngeal nerve testing depends on the underlying clinical condition and the patient’s symptoms. It is typically recommended to conduct the test when there is an indication of glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction or as part of a comprehensive neurological examination. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the appropriate frequency of testing in an individual case.
What to Do in Case of Abnormal Results?
If the glossopharyngeal nerve examination yields abnormal results, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a neurologist specialized in nerve function disorders. They will further assess the patient’s clinical history, conduct additional tests if necessary, and develop a treatment plan based on the underlying cause of the abnormal results. Self-diagnosis or self-treatment is strongly discouraged, as it may lead to incorrect conclusions or delays in receiving appropriate medical care.
In conclusion, testing the glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial component of a comprehensive neurological examination. By understanding the anatomy and functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve, preparing adequately, following a step-by-step guide, interpreting the results accurately, and prioritizing patient safety, healthcare professionals can effectively assess and diagnose potential disorders associated with this vital cranial nerve. Patients experiencing symptoms related to taste, swallowing, or sensory deficits in the throat should consult with a medical professional for a proper evaluation.