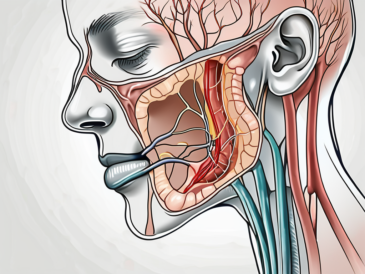
The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in the proper functioning of our throat and mouth. It is responsible for various key functions, including swallowing, taste sensation, and some aspects of speech. If you suspect any issues with your glossopharyngeal nerve, it is essential to undergo a thorough examination to assess its functioning. In this article, we will discuss the complete process of testing the glossopharyngeal nerve, from understanding its anatomy to interpreting the results. However, it is important to note that this article is for informational purposes only, and if you suspect any issues with your glossopharyngeal nerve, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a fascinating cranial nerve that plays a vital role in our daily lives. Let’s delve deeper into the anatomy and function of this intricate nerve.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, originates from the medulla oblongata, which is the lower half of the brainstem. This nerve is composed of both sensory and motor fibers, making it a versatile and complex structure.
The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve are responsible for transmitting taste signals from the posterior third of the tongue. This means that when you savor your favorite dish, it is the glossopharyngeal nerve that allows you to experience the delightful flavors. In addition to taste, these sensory fibers also provide sensation to the pharynx, tonsils, and soft palate, contributing to our ability to speak and perceive sensations in the throat region.
On the other hand, the motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve control the muscles involved in swallowing. These muscles work in perfect harmony to ensure that food and liquids pass safely from our mouths to our stomachs. Without the coordinated movements facilitated by the glossopharyngeal nerve, the simple act of swallowing would become a challenging and potentially dangerous task.
Role and Function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve’s role in the intricate process of swallowing cannot be overstated. It acts as the conductor, coordinating the movements of various muscles involved in swallowing. Through its motor fibers, this nerve ensures that the muscles contract and relax in perfect synchrony, allowing us to consume food and liquids without any complications.
But the glossopharyngeal nerve’s responsibilities extend beyond swallowing. It also plays a crucial role in our ability to taste. The sensory fibers of this nerve transmit taste signals from the posterior third of the tongue to the brain, allowing us to savor the flavors of our favorite meals. Whether it’s the sweetness of a ripe strawberry or the tanginess of a lemon, it is the glossopharyngeal nerve that enables us to experience these delightful sensations.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve provides sensory information from the pharynx, tonsils, and soft palate. This information contributes to our ability to speak and perceive sensations in the throat region. It allows us to detect changes in temperature, texture, and even pain, helping us navigate our daily lives with ease.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a remarkable cranial nerve that plays a crucial role in our everyday experiences. From tasting our favorite foods to facilitating the complex process of swallowing, this nerve is essential for our overall well-being. Understanding the anatomy and function of the glossopharyngeal nerve allows us to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that enable us to enjoy the simple pleasures of life.
Preparing for the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
Necessary Equipment for the Test
Before conducting the glossopharyngeal nerve test, it is crucial to gather the necessary equipment. This typically includes a tongue depressor, a penlight, gloves, sterile cotton swabs, and a stopwatch or a timer. These tools are essential for the healthcare professional to accurately assess the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
The tongue depressor is used to gently hold down the patient’s tongue, allowing the healthcare professional to have a clear view of the back of the throat. The penlight is used to illuminate the area, making it easier to identify any abnormalities or irregularities. Gloves are worn to maintain a sterile environment and prevent the spread of any potential infections.
In addition to these tools, sterile cotton swabs are used to stimulate the back of the throat, testing the patient’s gag reflex. This reflex is controlled by the glossopharyngeal nerve and is an important indicator of its proper functioning. Lastly, a stopwatch or timer is used to measure the patient’s response time to certain stimuli, providing valuable information about the nerve’s sensitivity and responsiveness.
Furthermore, it is essential for the healthcare professional performing the test to prioritize hygiene and cleanliness. Before beginning the procedure, they should thoroughly sanitize their hands using an appropriate disinfectant. This step helps minimize the risk of introducing any external contaminants that could interfere with the accuracy of the test results.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
To ensure accurate results, it is important for the patient to follow certain guidelines before the glossopharyngeal nerve test. These guidelines may include avoiding food or drink for a specific duration, depending on the test requirements.
The reason behind this fasting requirement is to prevent any potential interference that food or drink particles may have on the test results. By abstaining from consuming anything, the patient ensures that the back of their throat is clear and free from any residual substances that could affect the examination process.
However, it is important to note that the duration of fasting may vary depending on the specific instructions given by the healthcare professional. Factors such as the type of test being conducted and the patient’s individual circumstances can influence the length of the fasting period. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for specific instructions tailored to your individual case.
Following these patient preparation guidelines helps ensure that the glossopharyngeal nerve test is conducted under optimal conditions, allowing for accurate assessment and diagnosis. By adhering to these instructions, patients can contribute to the success of the test and facilitate the healthcare professional’s ability to provide appropriate care and treatment.
Conducting the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
Step-by-Step Procedure
The glossopharyngeal nerve test typically involves a series of simple steps to evaluate its functioning. The healthcare professional will begin by examining the patient’s mouth and throat to assess any visible abnormalities or signs of infection. They may use a tongue depressor to gently hold down the patient’s tongue, allowing for a clear view of the back of the throat. This examination helps the professional identify any redness, swelling, or unusual growths that may indicate issues with the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Once the initial examination is complete, the healthcare professional will proceed to test the patient’s swallowing abilities. They may ask the patient to swallow small amounts of water, carefully observing the throat for any signs of difficulty or abnormality during the swallowing process. The professional will pay close attention to the coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing, ensuring that the glossopharyngeal nerve is functioning properly.
In addition to assessing swallowing abilities, taste tests may also be conducted to evaluate the patient’s response to different flavors. The healthcare professional may use small amounts of sweet, sour, salty, and bitter substances to stimulate the taste buds on the back of the tongue. By observing the patient’s reactions and responses to these tastes, the professional can gather further information about the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Safety Measures during the Test
During the glossopharyngeal nerve test, healthcare professionals take various safety measures to ensure the patient’s well-being. They will carefully monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate and blood pressure, throughout the procedure. This continuous monitoring helps detect any changes that may indicate a negative reaction or potential complications.
Furthermore, any discomfort or adverse reactions experienced by the patient during the test will be promptly addressed by the healthcare professional. They will ensure that the patient is comfortable and provide necessary interventions to alleviate any discomfort or minimize potential risks.
It is important for the healthcare professional to maintain a sterile environment during the test. They will use disposable gloves and clean equipment to prevent the spread of infection. Proper hand hygiene will be practiced before and after the procedure to minimize the risk of contamination.
The healthcare professional will also communicate with the patient throughout the test, explaining each step and addressing any concerns or questions that may arise. This open communication helps establish trust and ensures that the patient feels informed and involved in their own care.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve test is a comprehensive evaluation of the nerve’s functioning. By conducting a thorough examination of the mouth and throat, assessing swallowing abilities, and performing taste tests, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the glossopharyngeal nerve’s health. The safety measures taken during the test, such as continuous monitoring of vital signs and prompt addressing of discomfort, prioritize the well-being of the patient. Through clear communication and a sterile environment, healthcare professionals ensure a positive and informative experience for the patient.
Interpreting the Results of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
The glossopharyngeal nerve test is a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve. This nerve plays a vital role in various essential functions, including swallowing, taste sensation in the posterior third of the tongue, and monitoring blood pressure. Interpreting the results of this test requires a comprehensive understanding of the normal functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
During the glossopharyngeal nerve test, the healthcare professional will perform a series of assessments to evaluate the nerve’s integrity and functionality. These assessments may include evaluating the patient’s ability to swallow, testing the sensation in the posterior third of the tongue, and monitoring blood pressure changes in response to specific stimuli. The results of these assessments are then compared to established standards to determine whether they fall within the expected range.
Normal vs. Abnormal Results
Normal results of the glossopharyngeal nerve test indicate that the nerve is functioning properly. In such cases, the patient will demonstrate the ability to swallow without difficulty, experience normal taste sensation in the posterior third of the tongue, and exhibit appropriate blood pressure responses to stimuli. These findings provide reassurance that the glossopharyngeal nerve is intact and operating as expected.
However, abnormal results of the glossopharyngeal nerve test may suggest potential issues or abnormalities that require further evaluation. For instance, if the patient experiences difficulty swallowing or exhibits altered taste sensation in the posterior third of the tongue, it may indicate dysfunction or damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve. Similarly, abnormal blood pressure responses, such as exaggerated or blunted reactions, may signal underlying neurological conditions affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Potential Disorders and Conditions
The glossopharyngeal nerve test serves as a valuable tool in identifying potential disorders or conditions that may affect the glossopharyngeal nerve. One such condition is glossopharyngeal neuralgia, a rare but debilitating condition characterized by severe throat, ear, and tongue pain. By assessing the patient’s ability to swallow and evaluating taste sensation, the glossopharyngeal nerve test can contribute to the diagnosis of glossopharyngeal neuralgia.
In addition to glossopharyngeal neuralgia, the glossopharyngeal nerve test can also help diagnose other conditions that may impact the glossopharyngeal nerve’s functioning. For example, dysphagia, a condition characterized by difficulty swallowing, may be identified through abnormalities in the swallowing assessment during the test. Furthermore, the test’s findings may provide valuable insights into underlying neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or tumors, that can affect the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Overall, the glossopharyngeal nerve test plays a crucial role in evaluating the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve and identifying potential disorders or conditions that may impact its integrity. By interpreting the test results in the context of established standards, healthcare professionals can provide accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans to address any abnormalities or dysfunctions detected.
After the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
After completing the glossopharyngeal nerve test, it is important to follow any post-test care instructions provided by the healthcare professional. This may include resting the throat, avoiding hot or spicy foods, and following any prescribed medication regimen if necessary. Taking these precautions can help minimize discomfort and promote healing.
Resting the throat is essential to allow the glossopharyngeal nerve to recover from the stimulation it underwent during the test. This means avoiding activities that strain the throat, such as excessive talking or singing. It is also advisable to avoid consuming hot or spicy foods, as they can irritate the throat and potentially exacerbate any discomfort or inflammation.
In addition to these general care instructions, it is crucial to closely follow any prescribed medication regimen. The healthcare professional may have prescribed medications to alleviate any pain or inflammation that may occur as a result of the test. Adhering to the prescribed medication schedule will help ensure optimal pain management and facilitate the healing process.
Although complications after a glossopharyngeal nerve test are rare, it is important to be vigilant for any unexpected symptoms or complications. If you experience severe pain, difficulty swallowing, persistent fever, or any other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare professional for further guidance. They will be able to assess your condition and provide appropriate recommendations or interventions if necessary.
Follow-up Procedures and Tests
In some cases, further evaluation or follow-up procedures may be necessary after the glossopharyngeal nerve test. This may involve additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging scans or specialized consultations with relevant specialists. These follow-up procedures are essential to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of any underlying conditions.
If further evaluation is recommended, the healthcare professional will explain the purpose and importance of the follow-up procedures. They will provide detailed instructions on how to prepare for the tests, including any dietary restrictions or medication adjustments that may be necessary. It is crucial to follow these instructions carefully to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
During the follow-up procedures, the healthcare professional will closely evaluate the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve and assess any potential abnormalities or underlying conditions. The results of these tests will guide the healthcare professional in developing an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Remember, following through with any recommended follow-up procedures is crucial for your overall health and well-being. By actively participating in your healthcare journey, you are taking an important step towards achieving an accurate diagnosis and receiving appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Glossopharyngeal Nerve Testing
Risks and Complications
The glossopharyngeal nerve test is generally considered safe, and the risks associated with it are minimal. However, as with any medical procedure, there may be potential risks and complications. These can include discomfort during the test, temporary sore throat, or mild allergic reactions to any substances used during the test. It is important to discuss any concerns or potential risks with your healthcare professional before undergoing the procedure.
Alternatives to the Glossopharyngeal Nerve Test
In certain situations, alternative diagnostic methods may be considered to assess the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve. These alternatives may include imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, or specialized consultations with neurologists or otolaryngologists. The choice of alternative methods depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history and the specific clinical presentation.
In conclusion, testing the functioning of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial step in evaluating the health of our throat and mouth. Through a comprehensive examination, healthcare professionals can assess any potential issues or abnormalities with the glossopharyngeal nerve, enabling accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of underlying conditions. However, it is important to remember that this article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you suspect any issues with your glossopharyngeal nerve, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance tailored to your specific needs.