The glossopharyngeal nerve is an important cranial nerve that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the human body. Pronouncing this term correctly can be a challenge for many individuals, especially those who are not familiar with medical terminology. However, with a little understanding and some helpful tips, anyone can confidently pronounce the term “glossopharyngeal nerve.”
Understanding the Term: Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Before we delve into the pronunciation, let’s take a moment to understand the term “glossopharyngeal nerve” itself. This cranial nerve is the ninth of the twelve cranial nerves and is responsible for carrying sensory and motor fibers to various areas, including the throat, tongue, and salivary glands.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is a complex and fascinating part of the human nervous system. It originates from the medulla oblongata, the lower part of the brainstem, and extends down through the neck and into the throat and tongue.
One of the primary functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve is to provide sensory information from the tongue, throat, and tonsils. This information is crucial for various processes, such as swallowing, taste perception, and even monitoring blood pressure.
Breaking Down the Word: Glossopharyngeal
To better understand how to pronounce “glossopharyngeal nerve,” let’s break the word down into its individual components. “Gloss-” refers to the tongue, “-pharyng-” relates to the throat, and “-eal” signifies the nerve itself. By understanding the meaning behind each part of the term, we can better comprehend its pronunciation.
The prefix “gloss-” comes from the Greek word “glōssa,” which means tongue. This part of the term emphasizes the nerve’s connection to the tongue and its role in facilitating taste sensation and movement of the tongue.
The combining form “-pharyng-” is derived from the Greek word “pharynx,” which refers to the throat. This component highlights the glossopharyngeal nerve’s involvement in swallowing and providing sensory feedback from the throat.
Lastly, the suffix “-eal” denotes that we are specifically referring to a nerve. This suffix is commonly used in medical terminology to indicate a nerve’s presence or involvement in a particular area of the body.
The Meaning Behind the Term
When we put the components together, “glossopharyngeal” can be thought of as the nerve that relates to the tongue and throat. This nerve plays a vital role in functions such as swallowing, taste sensation at the back of the tongue, and monitoring blood pressure.
Understanding the term “glossopharyngeal nerve” not only helps us grasp its pronunciation but also provides insight into its significance within the human body. The intricate connections between the tongue, throat, and nervous system are essential for our ability to eat, taste, and communicate effectively.
Next time you hear or read the term “glossopharyngeal nerve,” you can appreciate the complexity and importance of this cranial nerve and its role in maintaining our overall well-being.
Phonetic Breakdown of Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Now that we have a basic understanding of the term, let’s move on to the phonetic breakdown of “glossopharyngeal nerve.” By breaking the term into syllables, we can simplify the pronunciation process.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a cranial nerve that plays a crucial role in the sensory and motor functions of the tongue, throat, and certain organs in the neck. Understanding how to pronounce its name correctly is essential for effective communication in the medical field.
Syllable by Syllable Pronunciation
The term “glossopharyngeal nerve” can be broken down into four primary syllables: “glos-so-phar-yn-ge-al nerve.” To pronounce it correctly, let’s focus on each syllable individually:
- Glos- Pronounced as “glawss,” similar to the word “glossy.” This syllable represents the tongue, which is a key component of the glossopharyngeal nerve’s function.
- -so- Pronounced as “soh,” similar to the word “so.” This syllable represents the sensory aspect of the nerve, as it carries information from the tongue and throat to the brain.
- -phar- Pronounced as “far,” similar to the word “far.” This syllable represents the pharynx, which is the muscular tube that connects the mouth and the esophagus.
- -yn- Pronounced as “in,” similar to the word “in.” This syllable represents the sensory aspect of the nerve, as it carries information from the carotid body and sinus to the brain.
- -ge- Pronounced as “jee,” similar to the word “jeep.” This syllable represents the glossopharyngeal ganglion, which is a cluster of nerve cell bodies located near the base of the skull.
- -al Pronounced as “uhl,” similar to the word “all.” This syllable represents the nerve itself, which is responsible for various functions such as taste, swallowing, and salivation.
- nerve Pronounced as “nurv,” similar to the word “nerve.” This word signifies the overall structure and function of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
By pronouncing each syllable correctly and smoothly transitioning between them, you can confidently say “glossopharyngeal nerve.” Remember, proper pronunciation is not only important for effective communication but also for establishing credibility and professionalism in the medical field.
Common Mispronunciations and How to Avoid Them
Despite our best efforts, mispronunciations can still occur. Here are a few common mispronunciations of “glossopharyngeal nerve” and how to avoid them:
- Mispronunciation: “glah-so-fuh-RIN-gee-al nerve”
- Correction: Remember to pronounce each syllable distinctly, focusing on the correct sounds mentioned earlier. Pay attention to the “phar” and “ge” syllables, as they are often mispronounced.
- Mispronunciation: “glossy-pharyngeal nerve”
- Correction: Keep in mind that “glossy” is not the correct pronunciation of the first syllable. Instead, pronounce it as “glos” with a short “o” sound. This will help differentiate it from the word “glossy” and ensure accurate communication.
To ensure accurate pronunciation, it’s always helpful to hear the term spoken by a medical professional or consult with a healthcare provider. Additionally, practicing the pronunciation regularly can enhance your confidence and fluency when discussing the glossopharyngeal nerve and its related functions.
Tips for Pronouncing Medical Terms
Pronouncing medical terms can be challenging, but with some general rules, you can improve your pronunciation skills.
Medical terminology is a specialized language used in the healthcare field to describe various medical conditions, procedures, and treatments. It is essential for healthcare professionals to accurately pronounce these terms to ensure effective communication and patient care.
Here are a few general guidelines to follow when pronouncing medical terms:
- Break the word down into syllables and pronounce each syllable individually. This technique helps you focus on the different sounds and makes it easier to pronounce complex terms.
- Focus on the primary stress of the word, which usually falls on the first syllable. Understanding where the stress lies can significantly impact the pronunciation of a medical term.
- Pay attention to silent letters and unique vowel sounds. Some medical terms have silent letters or vowel combinations that create specific sounds. Being aware of these nuances can improve your pronunciation accuracy.
- Practice the pronunciation of medical terms regularly to improve your fluency. Repetition is key when it comes to mastering any skill, and pronunciation is no exception.
Remember, mastering medical term pronunciation takes time and practice, so be patient with yourself. Don’t get discouraged if you stumble over certain words initially. With dedication and perseverance, you will become more confident in your ability to pronounce medical terms accurately.
Techniques for Mastering Difficult Pronunciations
Some medical terms may prove more challenging than others. Here are a few techniques to help you conquer difficult pronunciations:
- Break it down: If a term seems overwhelming, break it down into smaller, manageable parts and practice each segment individually before combining them. By tackling the term in smaller chunks, you can gradually build up your confidence and improve your pronunciation.
- Listen to experts: Listening to audio recordings or seeking out pronunciations by healthcare professionals can be immensely helpful. Hearing how experts pronounce medical terms can provide you with a reference point and ensure accuracy in your own pronunciation.
- Use pronunciation resources: Utilize online resources, apps, or medical dictionaries that provide audio pronunciations of medical terms. These resources often break down the pronunciation into syllables and provide examples, making it easier for you to learn and practice.
Remember, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or consulting with a doctor can provide valuable insights into proper pronunciation and help clarify any doubts or concerns you may have. Don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance when needed.
By following these tips and techniques, you can enhance your ability to pronounce medical terms accurately. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep practicing and expanding your medical vocabulary to become a more proficient communicator in the healthcare field.
The Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Body
Now that we have covered the pronunciation of the glossopharyngeal nerve, let’s explore its critical role in the human body.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is an important component of the peripheral nervous system. It originates from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem, specifically from the posterior part of the medulla. This nerve is classified as a mixed nerve, meaning it contains both sensory and motor fibers, as well as parasympathetic fibers. This unique combination allows the glossopharyngeal nerve to carry out various functions throughout the body.
The Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
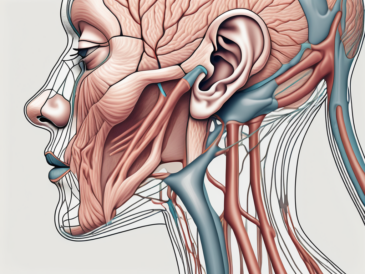
The glossopharyngeal nerve is composed of several branches that innervate different regions of the head and neck. One of its main branches, the tympanic nerve, provides sensory information to the middle ear, contributing to the sense of hearing. Additionally, the glossopharyngeal nerve sends branches to the stylopharyngeus muscle, which is involved in swallowing and the movement of food through the throat.
Another important branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve is the lingual branch, responsible for facilitating taste sensation at the back of the tongue. This branch carries taste fibers from the posterior one-third of the tongue, allowing us to perceive flavors such as bitter and sour.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve also plays a role in regulating blood pressure and heart rate. It contains sensory fibers that monitor blood pressure in the carotid sinus, a specialized area in the carotid artery. These sensory fibers transmit information to the brain, allowing it to make necessary adjustments to maintain cardiovascular homeostasis.
The Function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve performs several essential functions, including:
- Facilitating taste sensation at the back of the tongue: The lingual branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve carries taste fibers from the posterior one-third of the tongue, allowing us to experience a wide range of flavors.
- Aiding in swallowing and the movement of food through the throat: The glossopharyngeal nerve innervates the stylopharyngeus muscle, which helps in the process of swallowing and the movement of food from the mouth to the esophagus.
- Monitoring blood pressure and heart rate: The sensory fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve provide crucial information about blood pressure in the carotid sinus, enabling the body to regulate cardiovascular function.
- Providing sensory information related to the middle ear: The tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve supplies sensory fibers to the middle ear, contributing to our sense of hearing and balance.
- Controlling the secretion of saliva from the salivary glands: The glossopharyngeal nerve carries parasympathetic fibers that stimulate the secretion of saliva from the parotid gland, one of the major salivary glands in the mouth.
Understanding the role of the glossopharyngeal nerve highlights its significance in maintaining optimal bodily functions. From facilitating taste perception to regulating blood pressure, this nerve plays a crucial part in our overall well-being.
Recap: Pronouncing Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Let’s briefly recap some key points regarding the pronunciation of “glossopharyngeal nerve” and tips for mastering medical term pronunciation.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a complex structure responsible for various functions in the human body. It plays a crucial role in the sensation and movement of the tongue, throat, and other important areas.
When it comes to pronouncing “glossopharyngeal nerve,” it’s important to break the term into syllables and pronounce each syllable distinctly. This helps ensure clarity and accuracy in communication, especially in medical contexts.
Quick Review of Pronunciation Tips
To confidently pronounce “glossopharyngeal nerve,” remember the following:
- Break the term into syllables and pronounce each syllable distinctly.
- Pay attention to the correct sounds for each syllable, as mentioned earlier.
- Avoid common mispronunciations such as “glossy-pharyngeal nerve”.
- Consult healthcare professionals or pronunciation resources for guidance and clarification.
Mastering the pronunciation of medical terms requires practice and dedication. It’s a skill that can greatly enhance your ability to communicate effectively with colleagues, patients, and other healthcare professionals.
When encountering complex terms like “glossopharyngeal nerve,” it’s important to rely on reliable sources for guidance. Healthcare professionals and pronunciation resources can provide valuable insights and help you refine your pronunciation skills.
Final Thoughts on Pronouncing Medical Terms
Pronouncing medical terms accurately is essential for effective communication, particularly when discussing medical conditions or treatments. Clear and precise pronunciation ensures that information is conveyed accurately and avoids any potential misunderstandings.
While it may seem challenging initially, with practice and perseverance, anyone can improve their pronunciation skills. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals when in doubt, as accurate pronunciation is crucial in the medical field.
Now that you have a better understanding of how to pronounce “glossopharyngeal nerve” correctly, you can confidently discuss this crucial cranial nerve and its functions with others.
Exploring the intricate details of the glossopharyngeal nerve can be fascinating. This nerve not only provides sensory information from the tongue and throat but also contributes to the regulation of blood pressure and heart rate. Its involvement in the swallowing reflex and taste perception adds to its significance in the human body.
By expanding your knowledge of the glossopharyngeal nerve, you can appreciate the complexity and importance of this cranial nerve in various physiological processes. This understanding will enable you to engage in more meaningful discussions and contribute to the field of medicine.