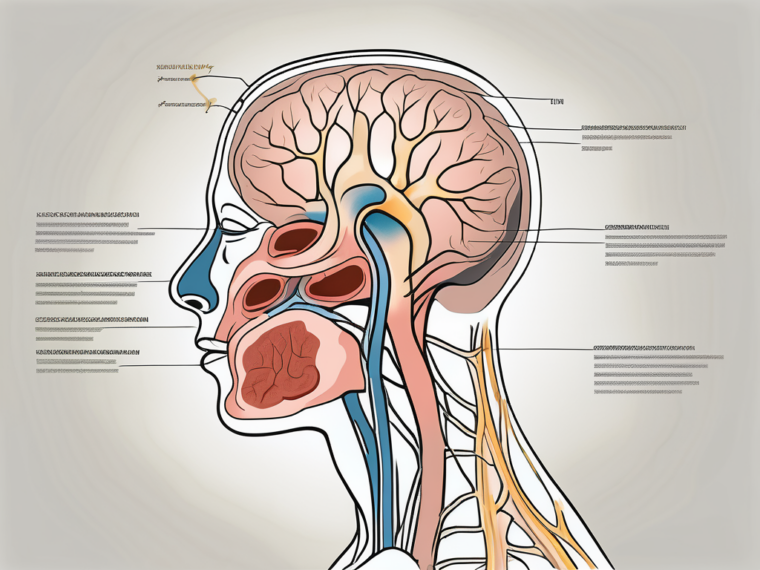
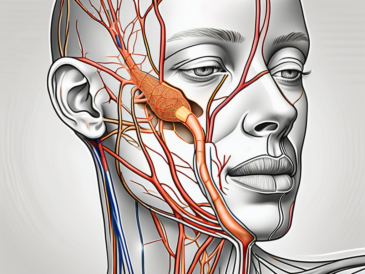
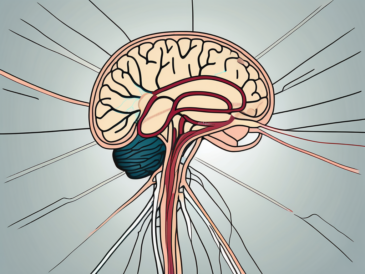
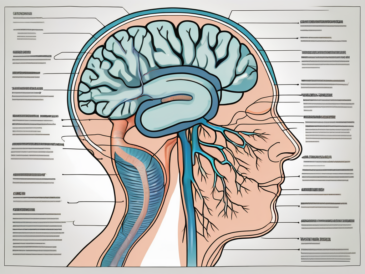
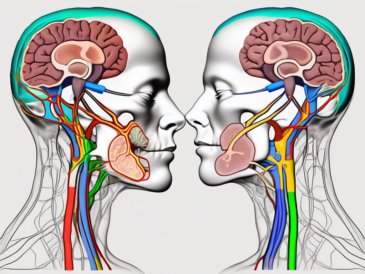
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in various functions within our bodies. It is an intricate network of nerves that innervates the tongue, throat, and other important structures. In this article, we will delve into the understanding of the glossopharyngeal nerve, its anatomy, functions, and the disorders associated with it. We will also explore the diagnosis, treatment, and the overall importance of maintaining the health of this vital nerve.
Understanding the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve is one of the twelve cranial nerves that emerge from the brainstem. It consists of both sensory and motor fibers, allowing it to transmit signals from the brain to the targeted areas, as well as relay sensations back to the brain. Understanding the intricate workings of this nerve is essential in comprehending its significance in the overall functionality of our bodies.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a complex and fascinating part of our nervous system. Let’s delve deeper into its anatomy and functions to gain a comprehensive understanding of its role in our everyday lives.
Anatomy of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve originates from the medulla oblongata, the lower portion of the brainstem. It consists of several branches that innervate different areas. One branch extends into the tongue, providing both taste sensations and general sensory information. This branch allows us to savor the sweetness of a ripe strawberry or the tanginess of a lemon. It also helps us detect temperature, touch, and pain in the oral cavity.
Another branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve reaches the throat, enabling functions such as swallowing and speech. This branch coordinates the movement of muscles involved in swallowing, ensuring that food and liquids pass safely from the mouth to the esophagus. It also plays a crucial role in the production of speech sounds, allowing us to articulate words with precision and clarity.
Additionally, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the production of saliva. It stimulates the salivary glands, ensuring that our mouths remain properly hydrated and aiding in the initial digestion of food. This function is vital for maintaining oral health and preventing conditions such as dry mouth or difficulty in swallowing.
Functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve performs a myriad of essential functions within our bodies. One of its primary duties includes its involvement in taste sensation. Through its sensory fibers, the glossopharyngeal nerve allows us to relish the flavors of our favorite foods and beverages. It not only helps us enjoy the sweetness of chocolate or the saltiness of potato chips but also facilitates the detection of bitter taste, thus playing a pivotal role in our gustatory experiences.
Furthermore, the glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for vital functions such as swallowing and speech. It coordinates the contraction of the muscles involved in the swallowing process, ensuring that food and drinks reach the stomach safely. Without the glossopharyngeal nerve, we would struggle to consume and digest our meals effectively.
In addition to its role in taste and swallowing, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial part in the regulation of blood pressure. It contains sensory fibers that monitor blood pressure levels and relay this information to the brain. This feedback loop helps maintain the stability of our cardiovascular system, ensuring that blood flow remains within optimal parameters.
Moreover, the glossopharyngeal nerve contributes to the regulation of respiration. It receives sensory input from the respiratory system, allowing the brain to monitor and adjust our breathing patterns as needed. This function is essential for maintaining a proper balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in our bodies.
As we can see, the glossopharyngeal nerve is a multifaceted and indispensable component of our nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and diverse functions highlight its significance in our daily lives and overall well-being.
The Role of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in the Body
The glossopharyngeal nerve serves as a vital component in our overall well-being. From our sensory experiences to our ability to communicate and maintain good oral health, this nerve’s impact is far-reaching.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, is one of the twelve cranial nerves originating from the brainstem. It emerges from the medulla oblongata, the lower part of the brainstem, and extends down the throat, innervating various structures in the head and neck region.
While the glossopharyngeal nerve is often overshadowed by its more famous counterpart, the vagus nerve, its functions are equally essential for our daily functioning.
Involvement in Taste Sensation
The role of the glossopharyngeal nerve in taste sensation is integral to our enjoyment of food and beverages. Without its contributions, our taste experiences would be significantly diminished.
The glossopharyngeal nerve carries taste information from the posterior third of the tongue, including the taste buds located on the back of the tongue. It transmits these signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive and differentiate between various flavors.
When the glossopharyngeal nerve is compromised or affected, it can lead to alterations in taste perception or even the loss of taste sensation altogether. This can have a profound impact on our quality of life, as the pleasure derived from eating and drinking is closely linked to our ability to taste. If you experience any concerning changes in your ability to taste, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate guidance.
Its Part in Swallowing and Speech
Swallowing and speech are essential aspects of our daily lives, enabling us to consume nourishment and communicate effectively. The glossopharyngeal nerve plays a significant role in coordinating the muscles involved in these processes.
During swallowing, the glossopharyngeal nerve helps to control the movement of the pharynx, the muscular tube connecting the mouth and the esophagus. It ensures that food or liquid is propelled in the right direction and prevents it from entering the airway, which could lead to choking or aspiration.
In addition to swallowing, the glossopharyngeal nerve also contributes to speech production. It helps to regulate the muscles involved in articulation, allowing us to form sounds and words accurately.
Issues with the glossopharyngeal nerve, such as damage or dysfunction, can result in difficulties swallowing or speaking. This can significantly impact a person’s ability to eat, drink, and communicate effectively. It is crucial to seek medical advice if you encounter persistent problems in these areas, as dedicated assessments and treatments may be necessary.
Contribution to Saliva Production
Saliva is essential for a healthy mouth, as it helps to cleanse the oral cavity, neutralize acids, and facilitate digestion. The glossopharyngeal nerve stimulates the salivary glands, contributing to saliva production.
The glossopharyngeal nerve innervates the parotid gland, the largest of the salivary glands, located near the ear. It sends signals to the gland, triggering the release of saliva into the mouth.
If there are disruptions in this nerve’s function, it can lead to dry mouth, also known as xerostomia. Dry mouth can cause discomfort, difficulty in chewing and swallowing, and an increased risk of dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is advised to address any salivary gland-related concerns. They can help identify the underlying cause of dry mouth and provide appropriate treatment options to alleviate symptoms and promote oral health.
Disorders Associated with the Glossopharyngeal Nerve
While the glossopharyngeal nerve plays essential roles in our bodies, it is not exempt from potential disorders that can affect its functionality.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that innervates the tongue, pharynx, and part of the ear. It is responsible for various crucial functions, including taste sensation, swallowing, and the reflexes involved in the gag reflex.
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition characterized by sudden, severe pain in the throat, ear, or base of the tongue. It is often triggered by activities such as swallowing, speaking, or even coughing. The pain experienced during glossopharyngeal neuralgia can be excruciating and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
The exact cause of glossopharyngeal neuralgia is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to irritation or compression of the glossopharyngeal nerve. This irritation can be caused by various factors, including blood vessels pressing against the nerve or the presence of tumors in the area.
If you suspect you may be experiencing glossopharyngeal neuralgia, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate pain management strategies. Treatment options may include medications to alleviate pain, nerve blocks, or in severe cases, surgical interventions to relieve pressure on the nerve.
Damage and Its Effects
Damage or dysfunction of the glossopharyngeal nerve can result from various factors, including trauma, infections, tumors, or systemic disorders. When the glossopharyngeal nerve is compromised, it can lead to a range of symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, altered taste perception, hoarseness, and a decreased production of saliva.
One of the most common causes of glossopharyngeal nerve damage is trauma, such as a car accident or sports injury. The forceful impact can injure the nerve, leading to pain and dysfunction. Infections, such as tonsillitis or abscesses in the throat, can also affect the glossopharyngeal nerve and result in symptoms like sore throat and difficulty swallowing.
Tumors in the vicinity of the glossopharyngeal nerve can also cause compression and damage. These tumors can be benign or malignant and may require surgical intervention for removal. Additionally, certain systemic disorders, such as diabetes or multiple sclerosis, can affect the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve as part of their broader impact on the nervous system.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is highly recommended to identify the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatment options. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a physical examination and possibly imaging studies, can help determine the extent of the damage and guide the development of a treatment plan.
Diagnosing and Treating Glossopharyngeal Nerve Issues
The glossopharyngeal nerve is a crucial cranial nerve responsible for various functions in the head and neck region. When issues arise with this nerve, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. Diagnosing and treating glossopharyngeal nerve issues require a comprehensive approach by healthcare professionals with expertise in neurology and otolaryngology.
Diagnostic Techniques
To accurately diagnose glossopharyngeal nerve issues, healthcare providers employ various diagnostic techniques. These techniques aim to identify the underlying cause of the symptoms and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
One of the initial steps in the diagnostic process is a thorough medical history evaluation. Healthcare professionals will inquire about the onset, duration, and progression of symptoms, as well as any relevant medical conditions or previous treatments. This information helps in narrowing down potential causes and determining the most appropriate diagnostic tests.
Physical examinations play a crucial role in assessing glossopharyngeal nerve function. Healthcare providers may perform a detailed examination of the head and neck region, evaluating muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes. They may also examine the throat and mouth to assess swallowing function and identify any abnormalities or signs of nerve dysfunction.
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the brain, head, and neck structures, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize any potential structural abnormalities or lesions affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Specialized tests may also be utilized to assess specific functions related to the glossopharyngeal nerve. These tests can include swallowing studies to evaluate the coordination and strength of the muscles involved in swallowing, taste perception tests to assess the nerve’s role in taste sensation, and saliva production tests to determine if there are any abnormalities in saliva production.
By combining the information gathered from medical history evaluations, physical examinations, imaging studies, and specialized tests, healthcare professionals can pinpoint the underlying cause of glossopharyngeal nerve issues and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options and Recovery
The treatment of glossopharyngeal nerve issues depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, conservative measures may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
Pain management techniques, such as medications or nerve blocks, can help reduce discomfort associated with glossopharyngeal nerve issues. Physical therapy may also be beneficial in improving muscle strength and coordination, especially in cases where nerve damage has caused swallowing difficulties or speech problems.
For more serious cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the specific issues affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve. Surgical procedures can range from nerve decompression, where pressure on the nerve is relieved, to nerve grafting or nerve repair techniques to restore function.
In addition to traditional treatment options, targeted therapies may also be considered. These therapies aim to address the underlying cause of the glossopharyngeal nerve issues, such as treating an infection or managing an autoimmune condition.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations based on your unique situation. They will consider factors such as the cause, severity, and impact of the glossopharyngeal nerve issues on your daily life when developing a treatment plan. With the right diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve issues can experience improved symptoms and enhanced quality of life.
The Importance of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve in Overall Health
The glossopharyngeal nerve holds significant importance in maintaining our overall health and well-being. Its proper functioning ensures our ability to taste, swallow, and speak effectively, as well as contribute to good oral health through adequate saliva production.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that originates in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. It consists of both sensory and motor fibers, making it crucial for various physiological processes in the head and neck region.
One of the primary functions of the glossopharyngeal nerve is to transmit taste sensations from the posterior one-third of the tongue. It carries information about the taste of food and beverages to the brain, allowing us to savor different flavors and enjoy the culinary experiences that enrich our lives.
In addition to its role in taste perception, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a vital role in coordinating swallowing and speech. It innervates the muscles involved in these processes, ensuring the smooth and efficient movement of food and the production of clear and intelligible speech.
Maintaining Nerve Health
To ensure the optimal health of the glossopharyngeal nerve and other cranial nerves, adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential. Practicing good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent dental issues that may affect the nerve’s function.
Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, especially vitamins B12 and B6, is crucial for nerve health. These vitamins play a significant role in maintaining the myelin sheath, a protective covering around nerve fibers that facilitates efficient nerve signal transmission.
Managing stress levels is also important for nerve health. Chronic stress can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which can negatively impact nerve function. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, exercise, and spending time in nature can help support the health of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Furthermore, refraining from habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is essential. These habits can damage nerve tissues and impair their proper functioning, leading to various health issues, including those related to the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Regular dental check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are also critical in detecting any potential issues early on. Dentists and doctors can assess the health of the glossopharyngeal nerve and provide appropriate guidance and treatment if necessary.
Impact on Quality of Life
The glossopharyngeal nerve directly influences our enjoyment of taste, our ability to communicate, and our oral health. Its impairments can significantly impact our quality of life, leading to discomfort, difficulties in social interactions, and limitations in our dietary choices.
Individuals with glossopharyngeal nerve disorders, such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, may experience severe pain in the throat, tongue, and ear regions. This pain can be triggered by activities such as swallowing, speaking, or even touching certain areas of the face. Such symptoms can greatly affect daily activities and overall well-being.
Moreover, the glossopharyngeal nerve plays a crucial role in saliva production. Adequate saliva production is essential for maintaining oral health, as it helps wash away food particles, neutralize acids, and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. Impairments in saliva production due to glossopharyngeal nerve dysfunction can lead to dry mouth, increased risk of dental decay, and difficulties in chewing and swallowing.
Recognizing the importance of the glossopharyngeal nerve in our everyday experiences emphasizes the need for prompt medical attention and proactive measures to preserve its proper functioning. Seeking early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms, improve overall quality of life, and prevent further complications.
In conclusion, the glossopharyngeal nerve performs vital functions in our bodies, such as facilitating taste sensations, coordinating swallowing and speech, and contributing to saliva production. Disorders associated with this nerve, such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia or damage, can have significant impacts on our well-being. Diagnosis and treatment require the expertise of healthcare professionals, who may utilize various diagnostic techniques and personalized treatment approaches. Maintaining the health of the glossopharyngeal nerve and other cranial nerves is essential for optimal functionality and overall quality of life. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms related to the glossopharyngeal nerve, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.